Navigating Emergencies with a Low-RF CARS
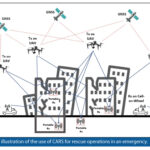
The prototype, consisting of a single Tx-Rx communication link, was tested in indoor-to-indoor, outdoor-to-outdoor and outdoor-to-indoor communication scenarios and in both static and dynamic conditions. The outdoor-to-indoor results indicate that, with further development, the Civilian and Assets Recovery System (CARS) is a promising navigation and positioning technology.
By Inside GNSS