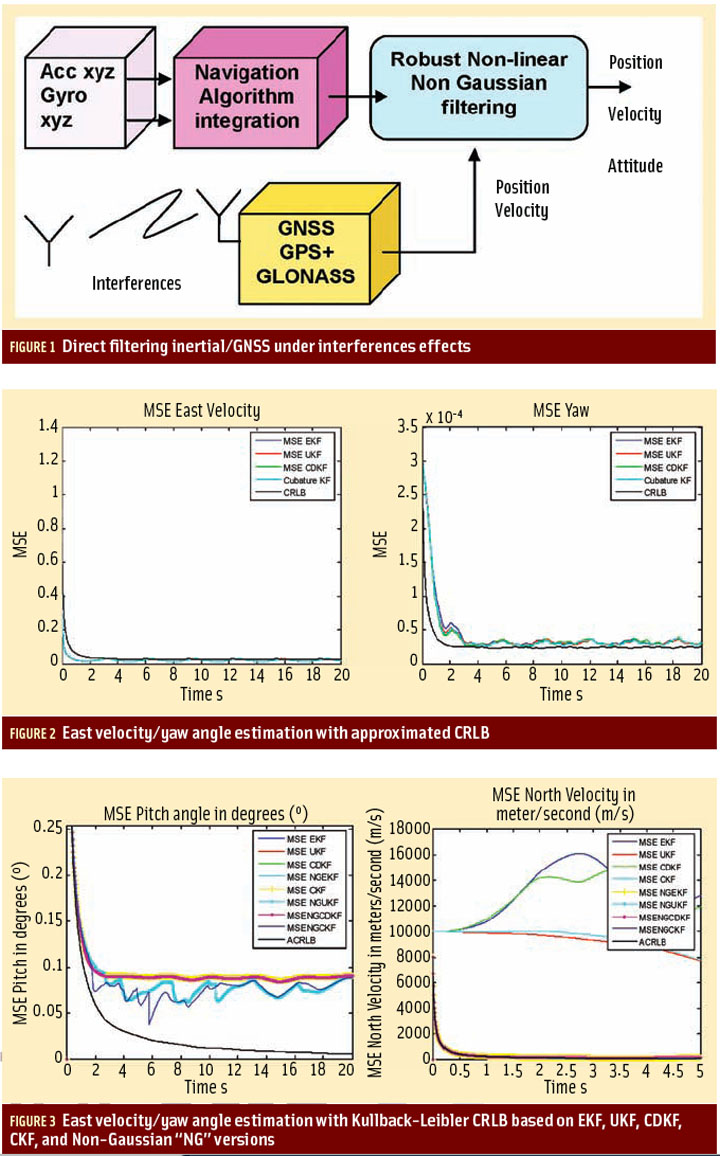
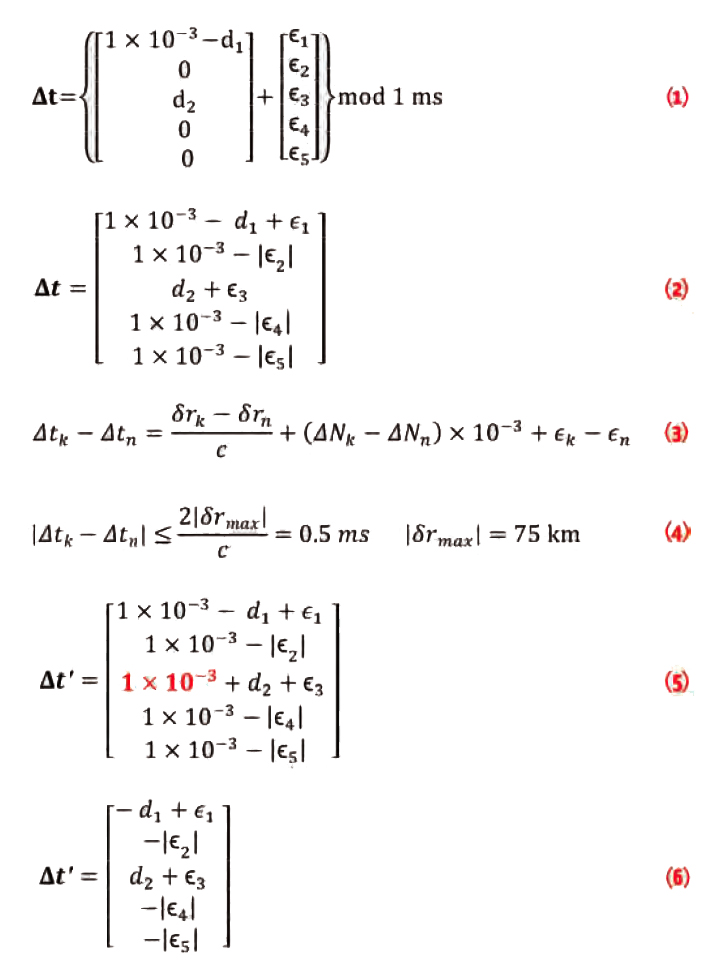
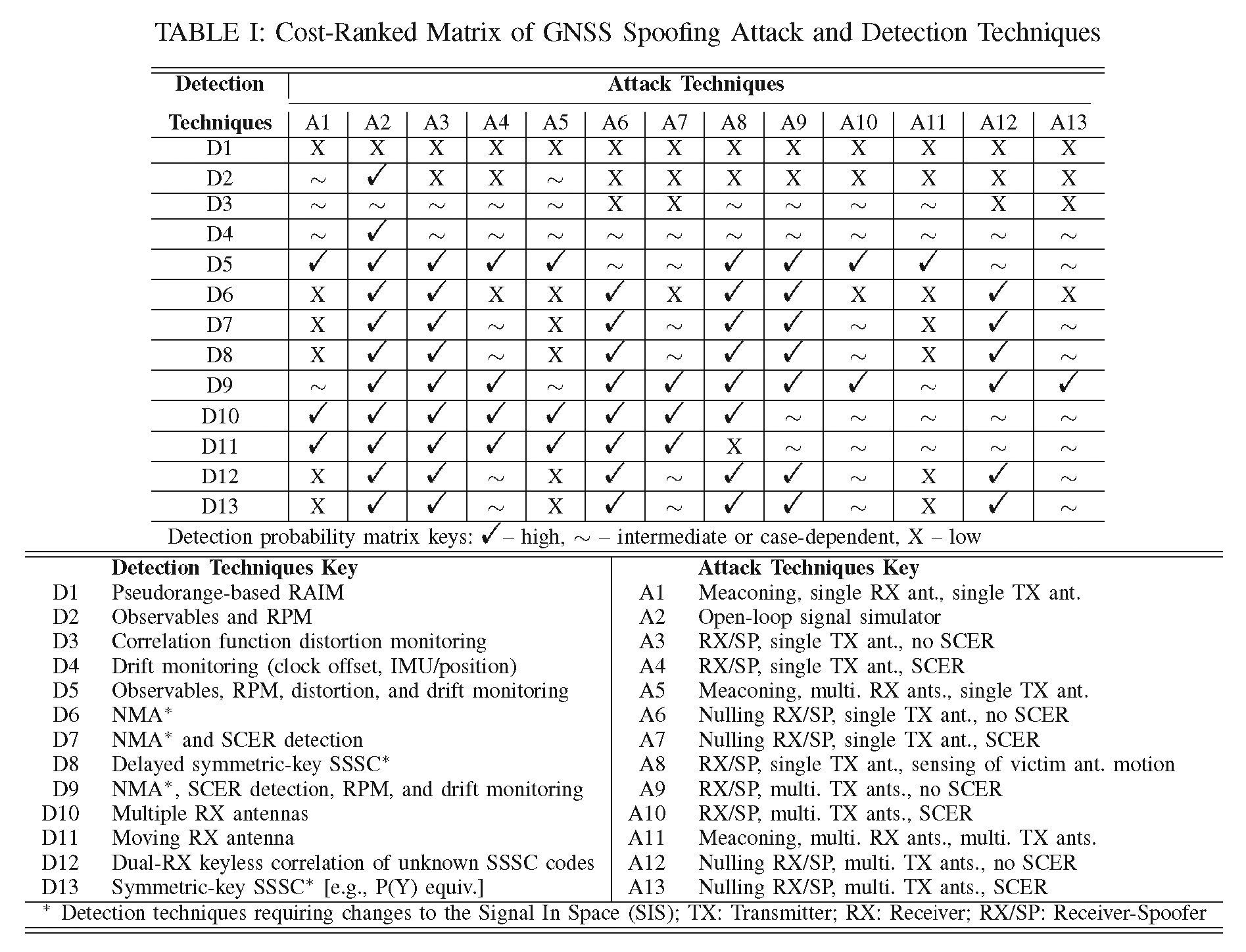
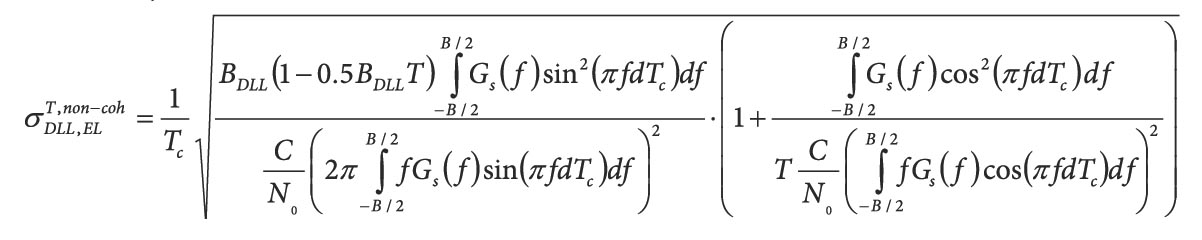Jade Morton’s Compass Points
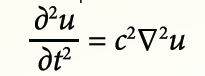 Jade Morton’s favorite equation
Jade Morton’s favorite equationReturn to main article: "Jade Morton: The Long and Scintillating Road"
COMPASS POINTS
Engineering specialties
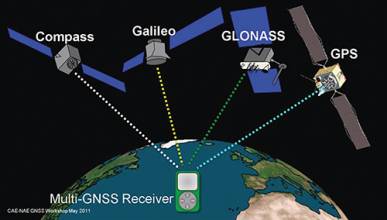
GNSS receiver data collection systems, GNSS receiver signal processing, GNSS for remote sensing of atmosphere and ionosphere, new navigation applications and technologies.
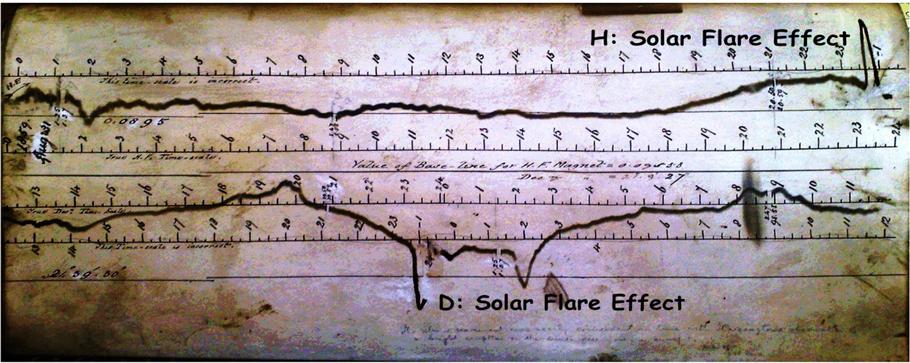
GNSS event that most signified to you that GNSS had ‘arrived’
By Inside GNSS