New Report Says Broadcom and Qualcomm Top GNSS IC Vendors
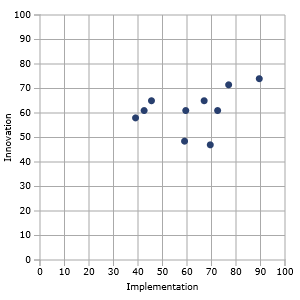 GNSS IC Vendor Competitive Assessment Vendor Matrix. Image Source: ABI Research.
GNSS IC Vendor Competitive Assessment Vendor Matrix. Image Source: ABI Research.A new reports says that the GNSS market landscape is growing because of rapid growth of satellite technology-enabled wearables, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), new innovation opportunities, and low-cost precision receivers.
ABI Research’s new GNSS integrated circuit (IC) vendor competitive analysis says that Broadcom and Qualcomm remain the two top companies for the fourth straight year.
By Inside GNSS


















_-_Sunset_-_2008-05-06-19-56-02.jpg)




