FAA Authorizes UAS Flights at Alaska Test Site
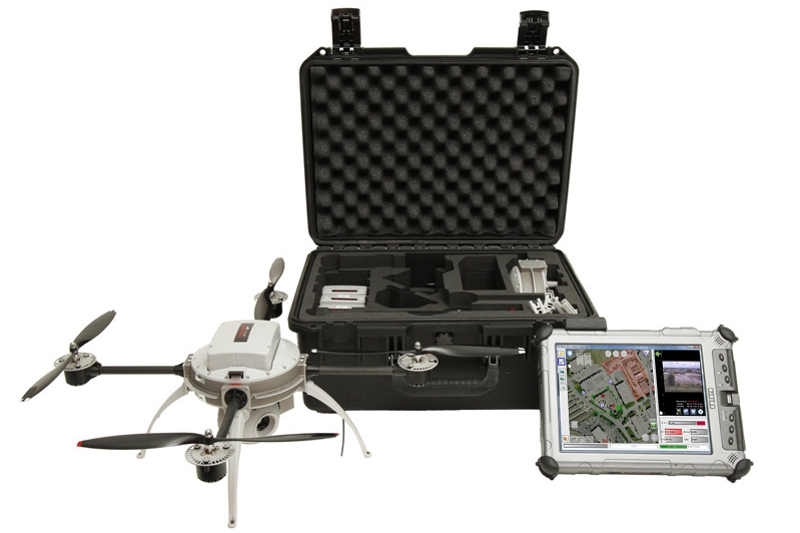 Aeryon Scout
Aeryon ScoutOn Monday (May 5, 2014), the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) announced that the University of Alaska’s unmanned aircraft system (UAS) test site has become operational — the second of six test organizations selected to take part in the congressionally mandated UAS in the National Airspace System (NAS) initiative that the agency is leading.
By Inside GNSS