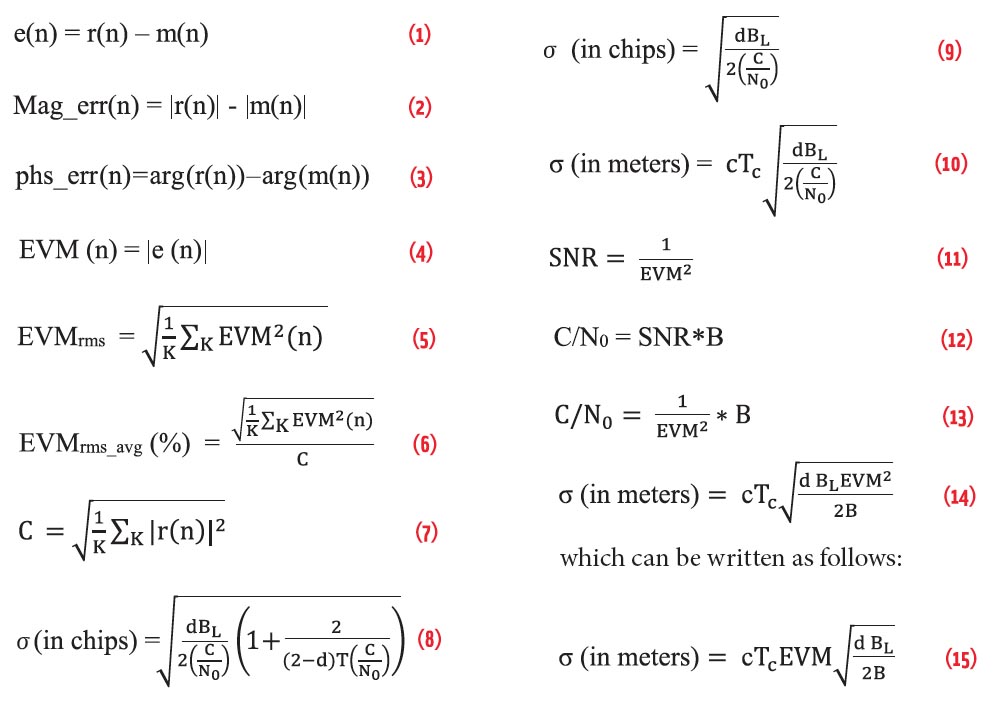
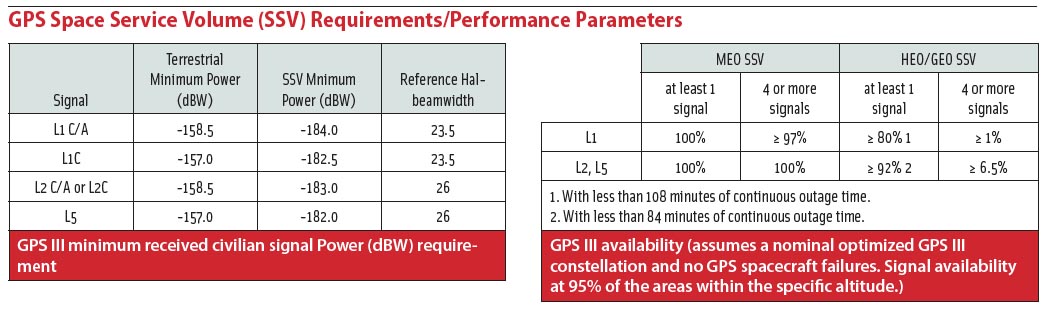
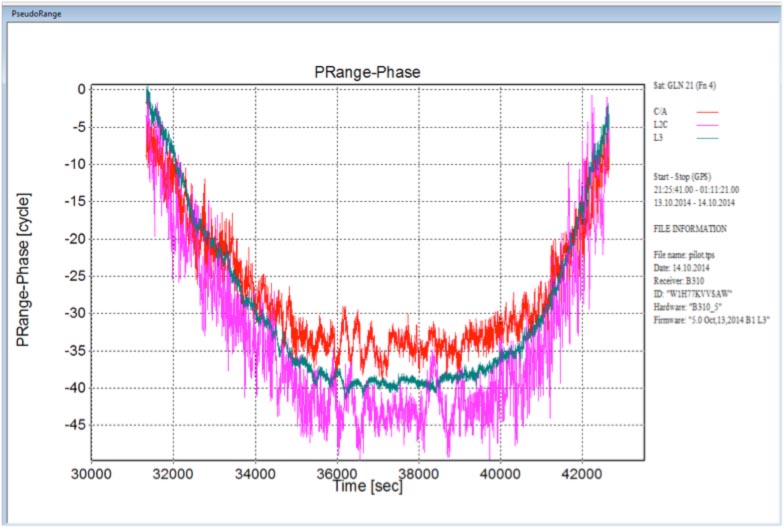
ION International Technical Meeting 2015

The Institute of Navigation’s 2015 International Technical Meeting will take place January 26-28 at the Laguna Cliffs Marriott Hotel in Dana Point California.
Online registration is available. Discounted Registration and hotel reservations end January 5.
By Inside GNSS