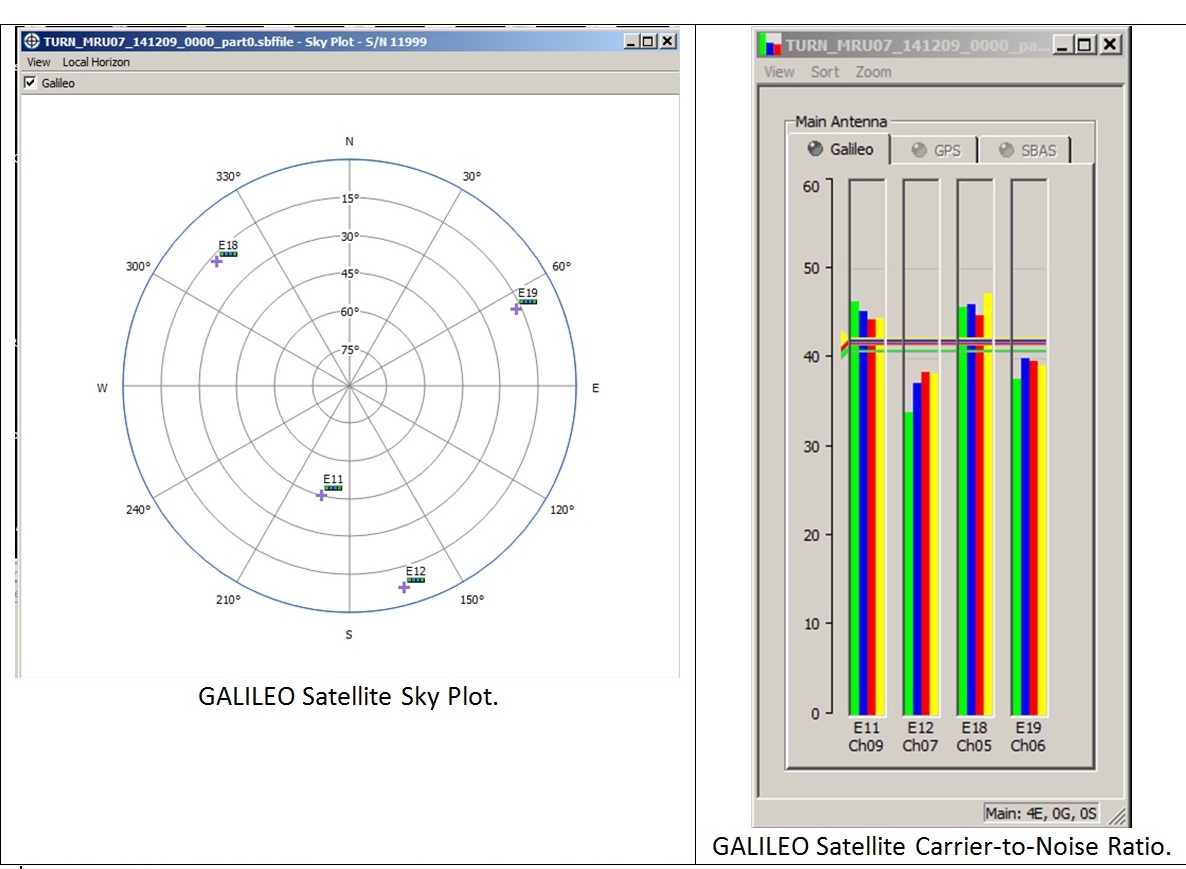
Sensonor’s STIM300 IMU Selected for Seabed’s New IMU
 Seabed’s SBD-IMU-S1 incorporates the Sensonor STIM300 IMU
Seabed’s SBD-IMU-S1 incorporates the Sensonor STIM300 IMUInstead of using the traditional fiber-optic gyros on which all its previous underwater systems have been based on, Seabed bv, based in Amsterdam, The Netherlands, has selected Sensonor’s STIM300 for its newest IMU, the SBD-IMU-S1.
By Inside GNSS