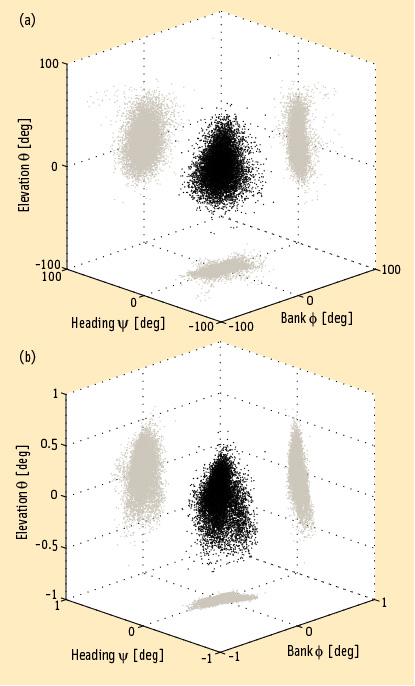
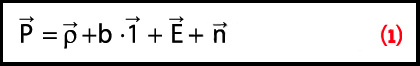GNSS Hotspots | September 2011
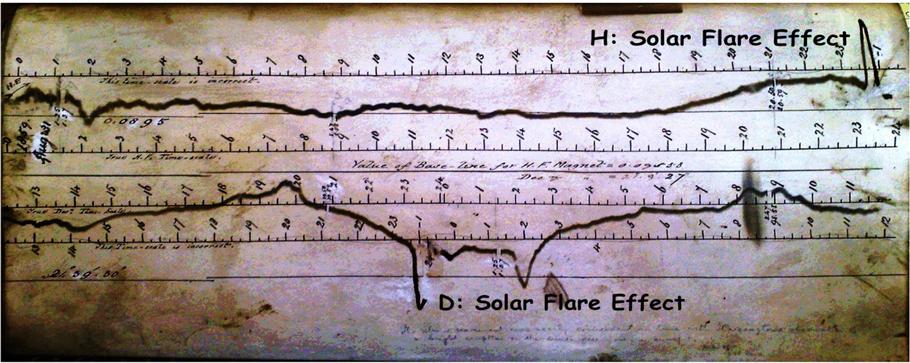 One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859
One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859 1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
 Nouméa ground station after the flood
Nouméa ground station after the flood A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat
A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
 Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated)
Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated) “Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto
“Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.
The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.  Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram
Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
1. HERE, KITTY KITTY
Santa Cruz, California USA
√ First, get the cougar on the treadmill . . . that’s what UC Santa Cruz researchers did to measure baseline behavior and design a tool that tells what puma concolor do every minute. Their super-advanced CARNIVORE collar uses GNSS and a 3-axis accelerometer to create a 24-hour diary of the wild life.