Keeping the Spoofs Out
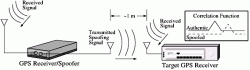
The demand for techniques capable of authenticating the GNSS signals and detecting simulation attacks (spoofing) has increased exponentially in the last years, mainly targeted to financial and safety critical applications.
Associated proposals and developments addressing these issues focused on two different approaches: user segment authentication services that leveraged existing services in order to detect signal spoofing and that integrated signal authentication services into the GNSS system itself.
By Inside GNSS