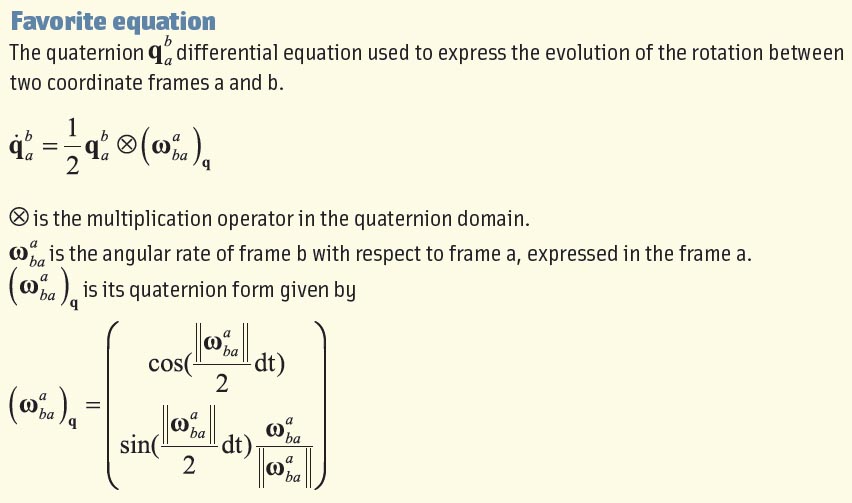
Can you list all the properties of the carrier-smoothing filter?
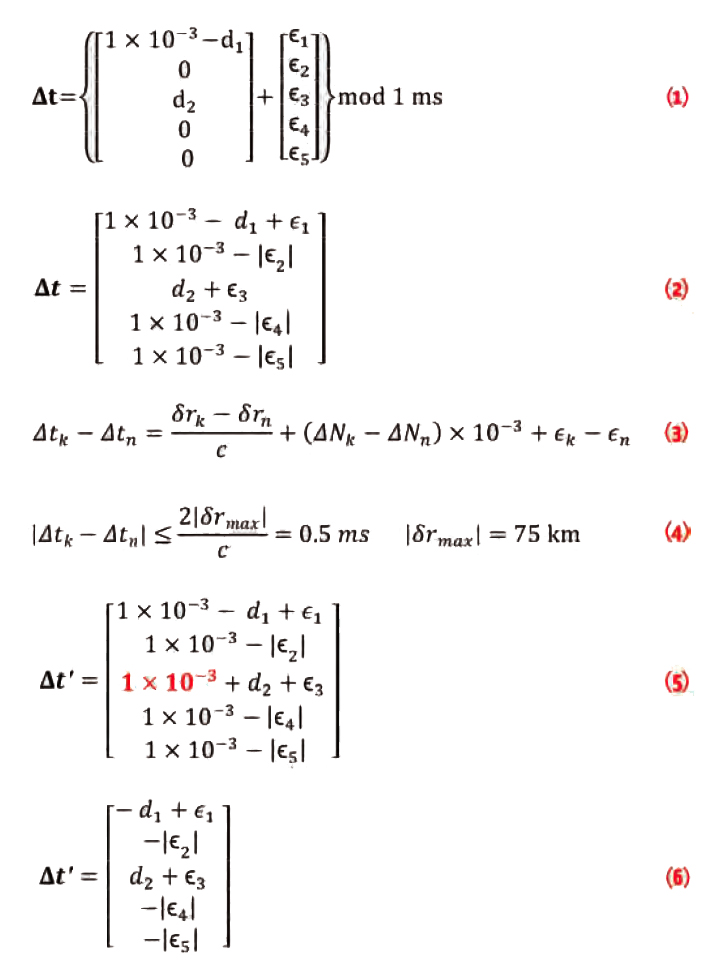
Q: Can you list all the properties of the carrier-smoothing filter?
A: Carrier-smoothing filters, also known as Hatch filters, are commonly used to reduce (“smooth”) the noise and multipath errors in pseudorange measurements by exploiting the high-precision relative distance information from carrier phase measurements. However, carrier-smoothing filters operate on more than just noise and multipath, and this article summarizes the response of such filters to all relevant inputs.
By Inside GNSS