Higher Aspirations for GNSS
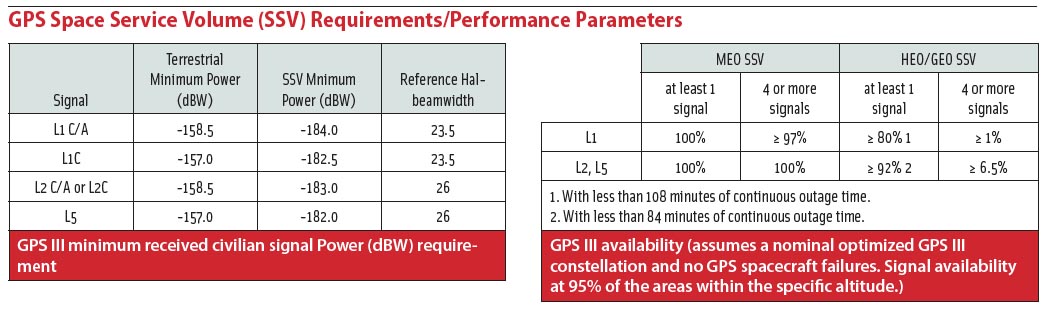 GPS Space Service Volume (SSV) Requirements/Performance Parameters
GPS Space Service Volume (SSV) Requirements/Performance ParametersNew space missions such as the robotic repair and recovery of damaged or errant communication satellites may become possible with the aid of an emerging class of receivers that is able to use GPS signals for navigation in orbits thousands of kilometers above the middle Earth orbit (MEO) GPS constellation itself.
By Dee Ann Divis