eCall
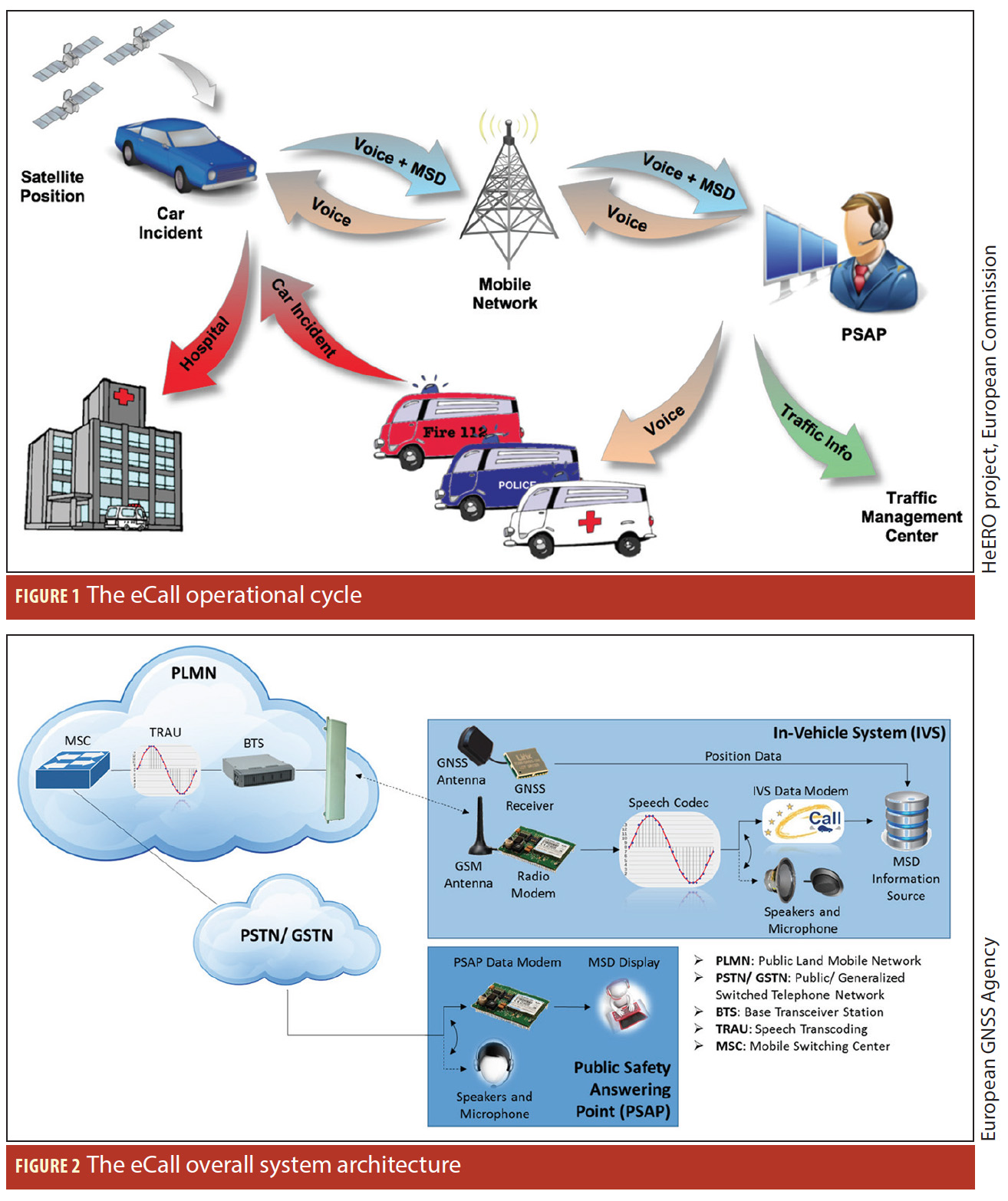 Figures 1 & 2
Figures 1 & 2On April 28, 2015, the European Parliament voted in favor of an eCall regulation, which requires all new models of passenger cars and light vans that will be certified for the European market to be equipped with the automated emergency-call technology beginning in April 2018. The measure applies to all such vehicles regardless of selling price. In the future, a similar service may be implemented for trucks as well.
By Inside GNSS