OxTS Launches WayFinder and LiDAR Boost for GNSS-denied Localization
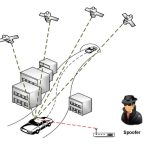
OxTS has launched WayFinder, a complete localisation solution for any environment, even GNSS-denied spaces. Functioning out of the box with no need for additional hardware, WayFinder uses a new, unique software called LiDAR Boost to provide accurate localisation both in, and between, any environment.
By Inside GNSS