Figures 5, 6 & 7: Reaching for the STARx
Return to main article: "Reaching for the STARx"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Reaching for the STARx"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Reaching for the STARx"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Reaching for the STARx"
By Inside GNSS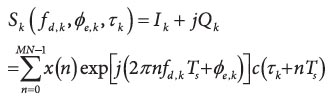 Equation 1
Equation 1GNSS modernization includes not only the global coverage capabilities of GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, but also regional GNSS enhancement systems such as Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), and the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS).
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Integrated Navigation"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Integrated Navigation"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Integrated Navigation"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Integrated Navigation"
By Inside GNSS GPS/BeiDou/MEMS configuration and GPS/MEMS configuration (left and right, respectively, top photo), Front view (center photo) and back view (lower photo) of nAX5.2
GPS/BeiDou/MEMS configuration and GPS/MEMS configuration (left and right, respectively, top photo), Front view (center photo) and back view (lower photo) of nAX5.2Due to the huge success of GPS in both military and civil applications, several other GNSSs have been developed, built, and operated in the last few decades. GNSS, regional, and augmentation systems are comprise a growing family that also includes GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, and Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS). New members, such as the Global Indian Navigation System (GINS), are preparing to join in next decade.
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "What’s Next for Practical Ubiquitous Navigation?"
By Inside GNSS