John Raquet’s Compass Points
 The Raquet family
The Raquet familyReturn to main article: John Raquet: A Family Affair
COMPASS POINTS
Engineering specialties
Navigation; navigation by signals of opportunity; sensor fusion/integrated avionics; GPS; navigation warfare; software development; stochastic estimation.
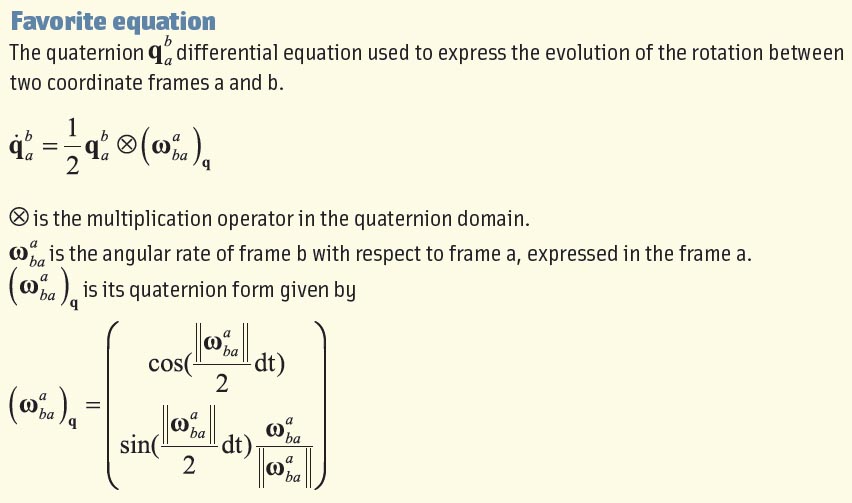
Favorite equation
eiπ = –1
By Inside GNSS