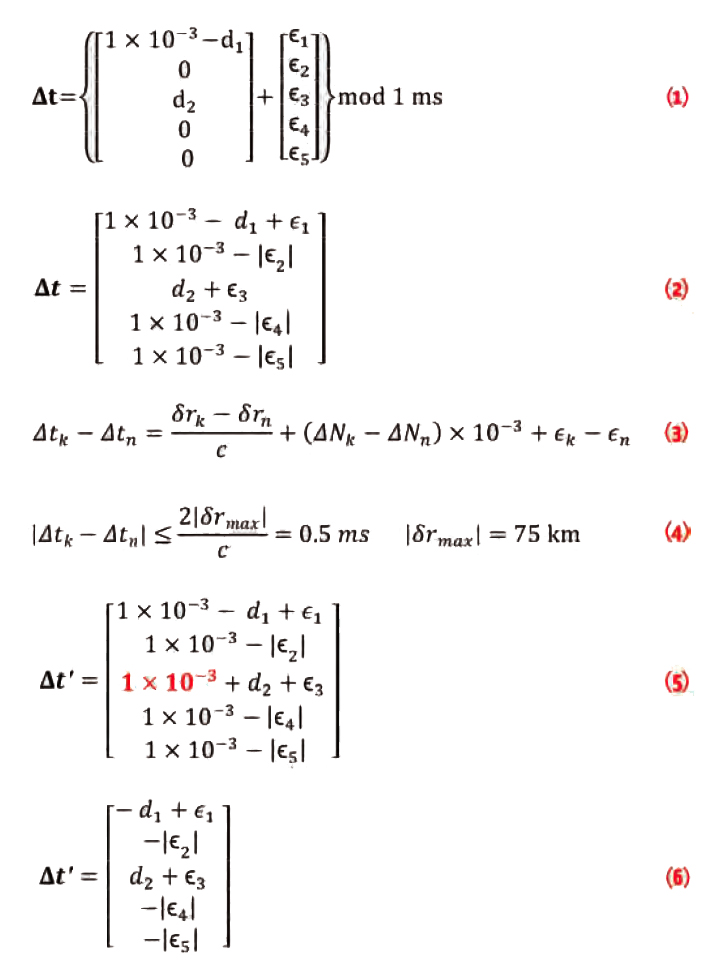
How does Earth’s rotation affect GNSS orbit computations?
GNSS positioning is premised on the idea that the satellite positions are known, or can be calculated. Errors in the computed satellite position will manifest as ranging errors that degrade the positioning accuracy.
By Mark Petovello