Measuring GNSS Signal Strength
Q: What is the difference between SNR and C/N0?
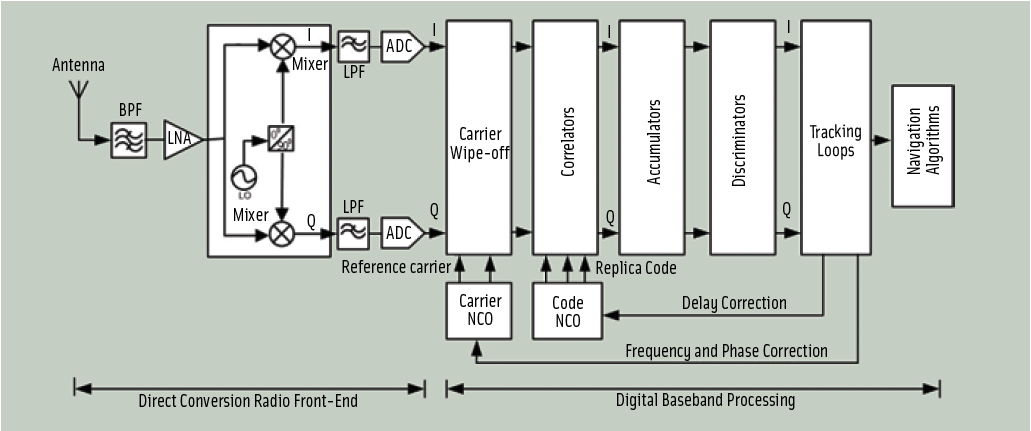
A: GPS receivers built for various applications, such as handhelds, automobiles, mobile phones, and avionics, all have a method for indicating the signal strength of the different satellites they are tracking. Some receivers display the signal strength in the form of vertical bars, some in terms of normalized signal strength, and others in terms of carrier-to-noise density (C/N0) or signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
By Inside GNSS