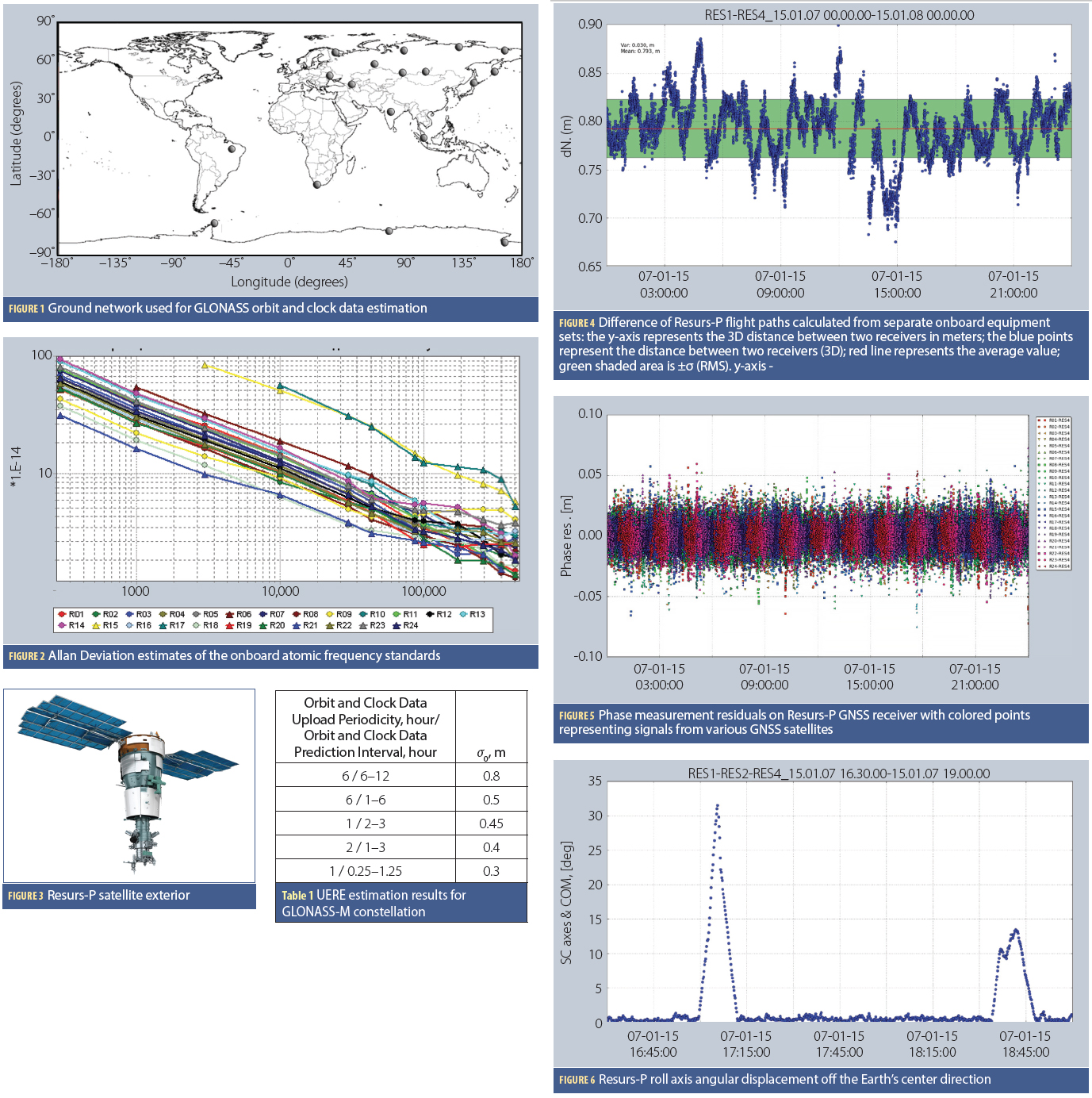
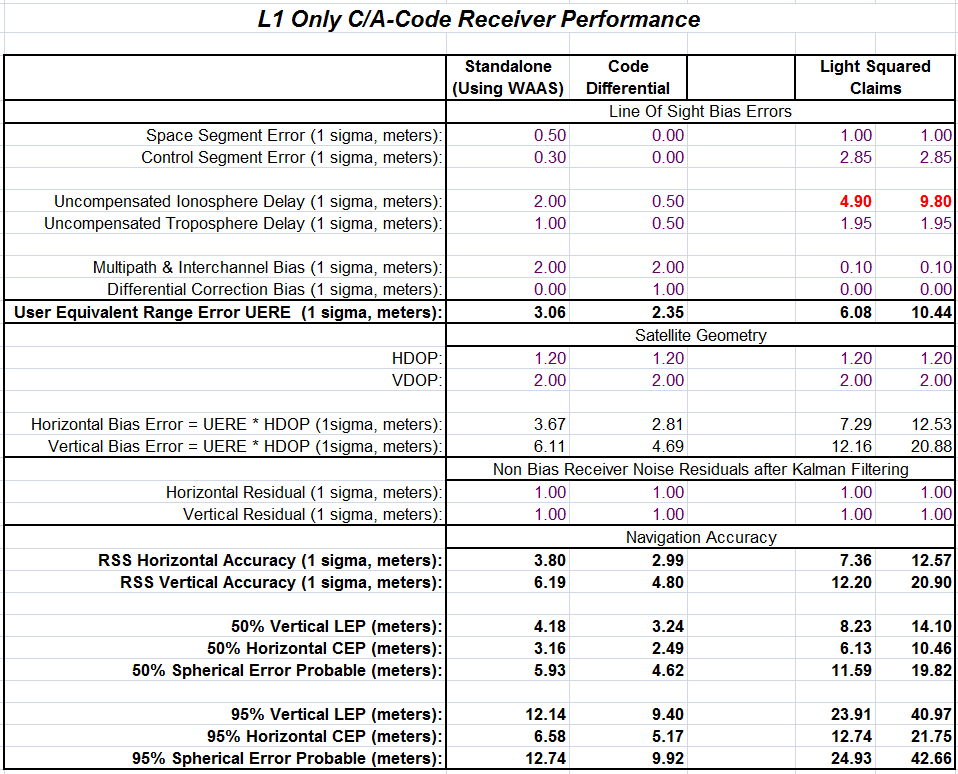
International Navigation Gathering Highlights GNSS Advances and Distractions
 Sergey Revnivykh
Sergey RevnivykhSpeakers at the recent International Association of Institutes of Navigation (IAIN) conference in Prague threw into stark relief some of the big GNSS programs and even bigger GNSS questions.
Prof.-Dr. Günter Hein, former head of the European Space Agency (ESA) EGNOS and GNSS Evolution Program Department and Emeritus of Excellence at University FAF Munich, delivered a fact-filled and level-headed presentation on the status of Galileo, the European Union’s civil-owned and non-military GNSS, with slides and information provided by ESA.