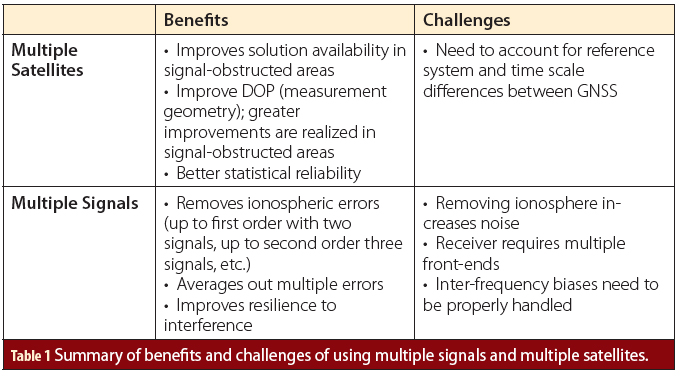
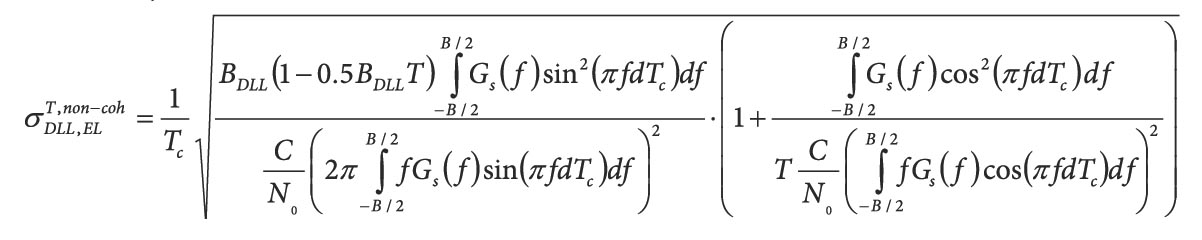Would you prefer to have more signals or more satellites?
Q: Would you prefer to have more signals or more satellites?
A: This is somewhat of a classic GNSS question, but before getting to the answer, let’s seek some clarity about what is being asked. First, by definition, “more” signals or “more” systems must be referenced against some baseline configuration. This is commonly assumed to be a GPS L1 C/A solution, and this assumption is also used herein.
By Inside GNSS