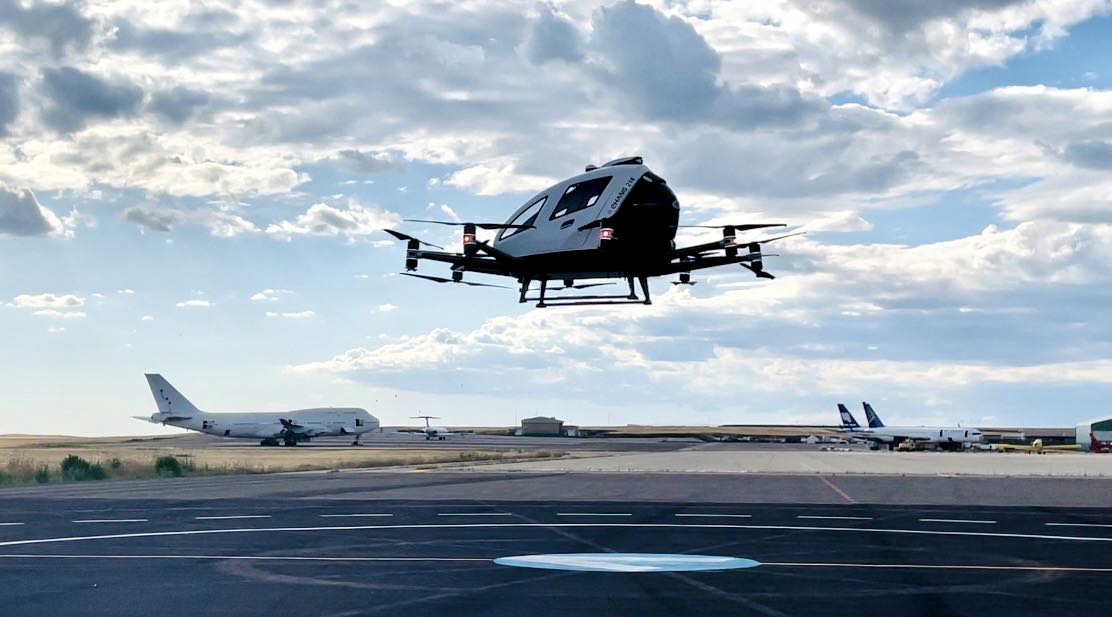
The EU-funded SAMVA project recently completed a series of successful electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft flights at the first EGNOS-enabled ‘vertiport’, at Lleida–Alguaire International Airport in Catalonia, Spain.
Project partners used EGNOS, which stands for the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service. It is the EU’s satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS), to ensure precise and accurate positioning during the flights. The vehicle was a a two-passenger multicopter made by EHang, production model EH216-S. Among other things, SAMVA partners developed, tested and validated new, first-flight, procedure design criteria for autonomous eVTOL passenger aircraft based on EGNOS.
The achievement highlights progress being made in integrating EGNOS satellite-based capabilities in eVTOL flight operations. It also paves the way towards incorporating these vehicles within U-Space, the set of new European services designed to support safe, efficient and secure access to airspace for large numbers of drones.
The SAMVA project (SBAS adoption in multicopter VTOL aircraft) is partly funded by the European Union Agency for the Space Program (EUSPA) and is led by engineering firm PildoLabs. In a recent communication, the company’s CEO Santiago Soley called the project a significant step forward in integrating satellite navigation into urban air mobility, enhancing safety and efficiency and placing European airspace at the forefront in the push to get eVTOL technologies up and flying. Jordi Candela, Director of Aeroports de Catalunya, called the successful SAMVA flights a milestone in advancing urban air mobility in Europe.
The key objectives of the SAMVA project include:
- Enhancing Emergency Medical Services: Implementing the first Point-in-Space and Low-Level-Route operations in Spain to improve Helicopter Emergency Medical Services.
- Deployment at Lleida-Alguaire Airport: Launching the first EGNOS services for eVTOL operations, demonstrating EGNOS’s capability in supporting airspace integration and Air Traffic Management tasks
- Advancing Safety-of-Life Services: Showcasing how current and future EGNOS services can support eVTOL integration in challenging operational environments by integrating data from onboard sensors.
- Precision Navigation Capabilities: Enabling precise guidance and supporting airspace integration for autonomous eVTOL aircraft.
- Validating Flight Procedures: Developing, testing, and validating a first flight procedure design criteria for autonomous eVTOL passenger aircraft based on EGNOS.
Using Any and All Means
Part of EUSPA’s aim in supporting SAMVA is to promote the more rapid uptake of EGNOS capabilities by rotorcraft manufacturers, operators and service providers, including providers of medical and other safety-, search- and rescue-related services. The agency is continuing to develop EGNOS products, to be used in combination with the Galileo High Accuracy Service (HAS), to provide the highest possible levels of accuracy and integrity for autonomous eVTOL operations.
The SAMVA project is now focused on further exploring how current, leading-edge navigation technologies and services, including the EGNOS Safety-of-Life Service, can be used in optimized eVTOL operations, especially in challenging urban environments, including through the fusion and hybridization of data from on-board sensors.
Certainly, the still youthful eVTOL industry is growing rapidly, gaining investment in what is now widely seen as a revolutionary technology that could radically transform air transport in the near future. Work under SAMVA brings that promise closer to fruition.