What is Doppler collision and is it a problem in GNSS?
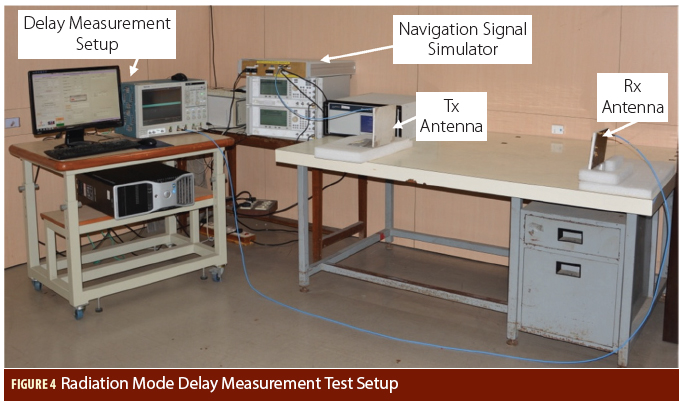
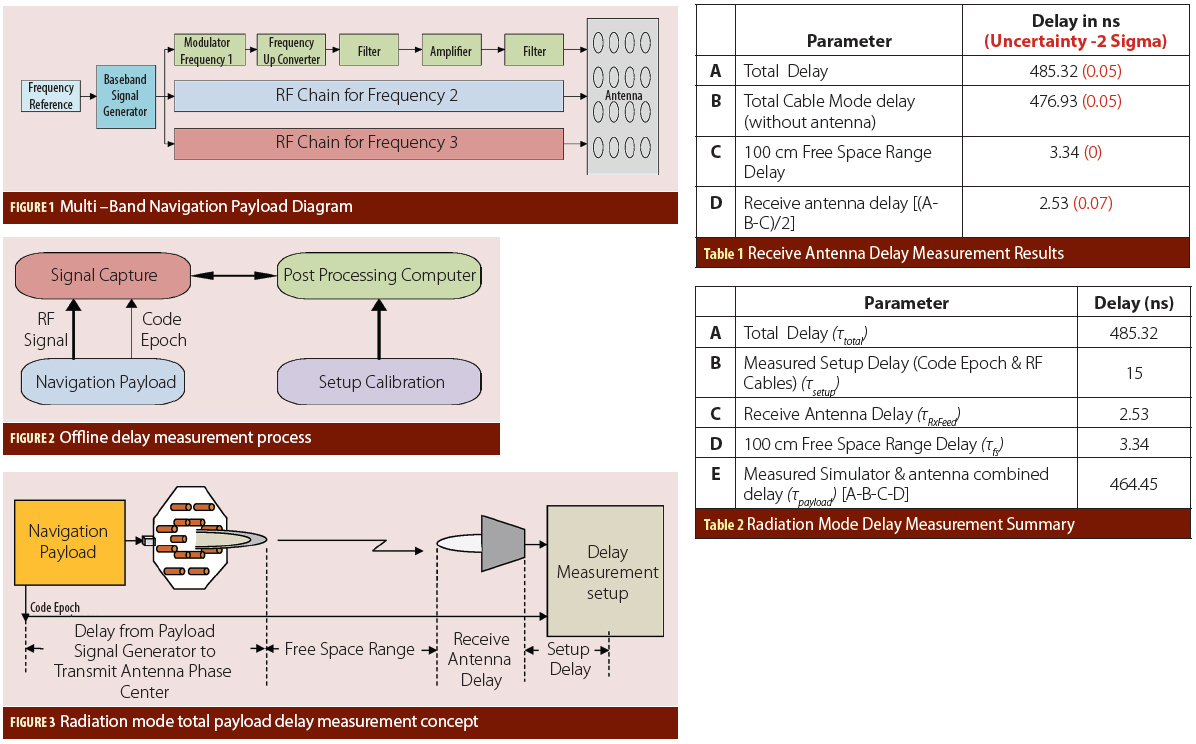
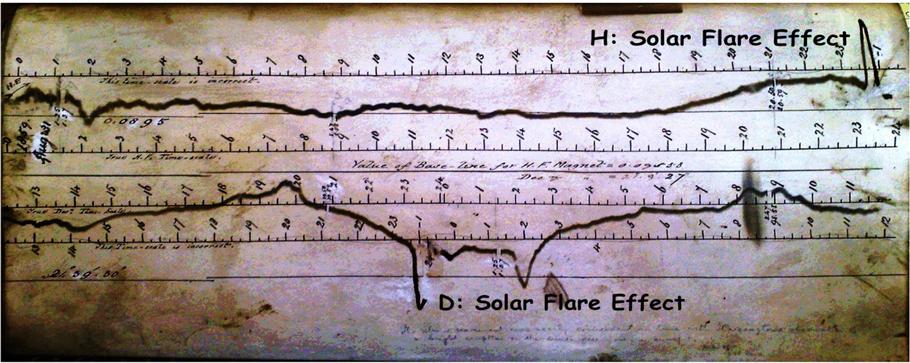
 Figure 1, 3, 4 & 5
Figure 1, 3, 4 & 5Q: What is Doppler collision and is it a problem in GNSS?
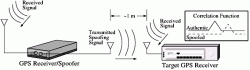
A: Doppler collision is a physical effect in code-division multiple access (CDMA) systems where code measurement errors are observed due to cross-correlation effects. Doppler collision may occur when the Doppler frequency between signals from two different transmitters is smaller than the code lock loop bandwidth.
By Inside GNSS