Shift to the Cloud at the Core of Restaged OCX Program

Key details are emerging about how Air Force managers are working to pull into line the substantially delayed and over budget program to build a new GPS ground system.
By Inside GNSS
Key details are emerging about how Air Force managers are working to pull into line the substantially delayed and over budget program to build a new GPS ground system.
By Inside GNSS GPS III SV01 now awaits a call up to begin pre-launch preparations. Photo: Lockheed Martin.
GPS III SV01 now awaits a call up to begin pre-launch preparations. Photo: Lockheed Martin.Ushering in a new era of advanced Global Positioning System technology, the U.S. Air Force this week declared the first Lockheed Martin-built GPS III satellite “Available for Launch.”
The Air Force’s “AFL” declaration is the final acceptance of Lockheed Martin’s first GPS III Space Vehicle (GPS III SV01) prior to its expected 2018 launch. GPS III SV01 will bring new capabilities to U.S. and allied military forces, and a new civil signal that will improve future connectivity worldwide for commercial and civilian users.
By Inside GNSSThe nation’s leading satellite navigation experts have invited Ligado Networks, a firm whose plans are widely viewed by many as a threat to satnav, to present at their November 15 meeting. If the company accepts, it could illuminate the structure of the terrestrial service it has in mind and either ease, or add fuel to, the ongoing dispute between Ligado and the GPS community.
By Dee Ann Divis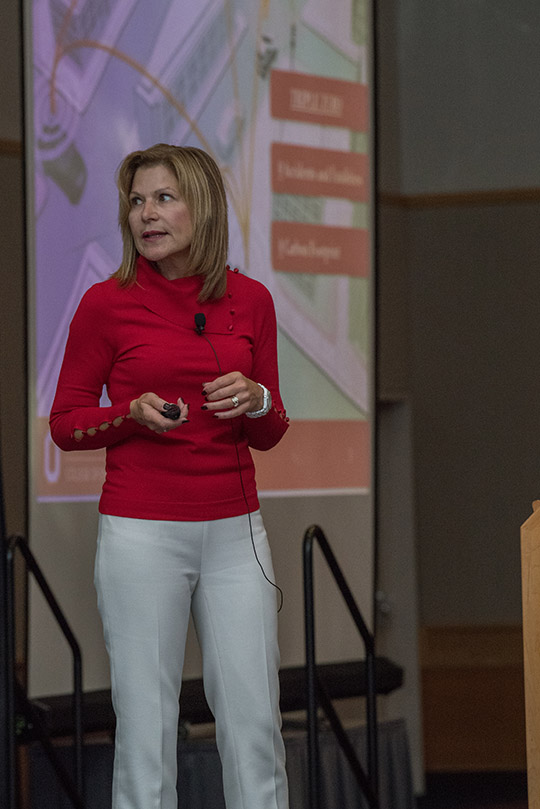 Carla Bailo, AVP for mobility research and business development at OSU, spoke at ION GNSS+ on Sept. 26. Photo: Institute of Navigation.
Carla Bailo, AVP for mobility research and business development at OSU, spoke at ION GNSS+ on Sept. 26. Photo: Institute of Navigation. If all goes as planned, Columbus, Ohio will become one of the smarter cities around, using drones to deliver medical supplies, autonomous shuttles for college students, and a smart infrastructure that will help with buses, traffic congestion, collision avoidance for both vehicles and pedestrians, and much more.
By Inside GNSS General John (Jay) Raymond
General John (Jay) Raymond The ground was already shifting when Gen. John (Jay) Raymond took charge of Air Force Space Command (AFSPC) in October 2016. Just six months before, his predecessor Gen. John Hyten had announced the Space Enterprise Vision, a new way of approaching space asset development, management and protection now that space had become both contested and far more crowded. There were issues across the space, ground and user segments of the GPS program; sequestration was still looming and Congress was looking closely at how to reorganize the way the Air Force managed its space programs.
By Inside GNSS Martin Faga, a former assistant secretary of the Air Force for space. GPS.gov photo.
Martin Faga, a former assistant secretary of the Air Force for space. GPS.gov photo.The battle lines over restructuring the management of military space were drawn sharply Sept. 18 when the Senate passed its version of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2018.
By Inside GNSS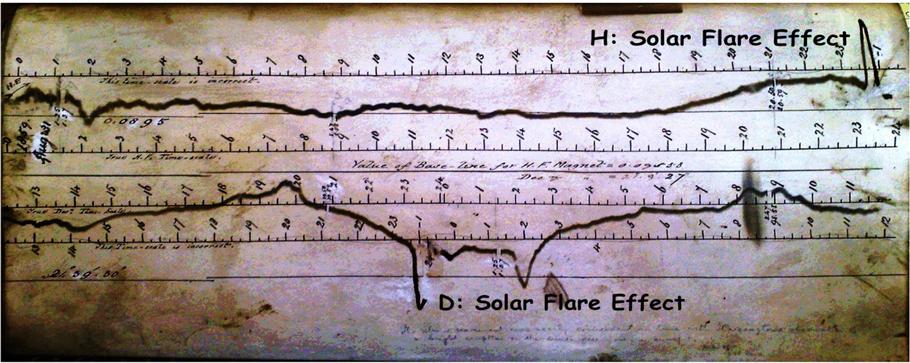 One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859
One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859 1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
 Nouméa ground station after the flood
Nouméa ground station after the flood A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat
A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
 Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated)
Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated) “Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto
“Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.
The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.  Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram
Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
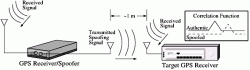
1. Mangrove Tree-Planting Drones
Myanmar (Southeast Asia)
Denver, Colorado-based Lockheed Martin announced that the U.S. Air Force awarded the company a $45.5 million contract to provide Military Code (M-Code) Early Use (MCEU) capability to the Global Positioning System (GPS). Part of the Air Force’s overall modernization plan for the GPS, M-Code is an advanced, new signal designed to improve anti-jamming and protection from spoofing, as well as to increase secure access, to military GPS signals for U.S. and allied armed forces.
By Inside GNSSNavigating the globe was once done using the sun, moon and stars as references, but modern times bring modern methods, and the majority of the world now relies on GPS — or another GNSS — for its navigation needs.
But what happens when GPS isn’t available?
A collection of Department of Defense (DoD) units and U.S. universities recently found out when they gathered at Edwards Air Force Base to evaluate various aerial platforms in a degraded GPS environment.
By Inside GNSSAfter several years of shifting plans the competition to build the next tranche of GPS III satellites is poised to start, though the context in which that contest will take place has changed markedly from when planning first began.
By Dee Ann Divis Bernhard Richter, Leica Geosystems GNSS business director
Bernhard Richter, Leica Geosystems GNSS business director Enrico Salvatori, Qualcomm Europe
Enrico Salvatori, Qualcomm Europe Carlo Bagnoli, STMicroelectronics
Carlo Bagnoli, STMicroelectronicsMultinational semiconductor and telecommunications company Qualcomm is a world leader in the design and marketing of 3G, 4G and next-generation wireless technologies. Headquartered in San Diego, California, Qualcomm has been widening its footprint in the Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) region, with a core focus in Europe.
“We expect to grow Qualcomm’s presence in Europe, becoming a major EU (European Union) player in the digitization of European industries,” said Qualcomm senior vice president and president of Qualcomm Europe, Enrico Salvatori.
By Inside GNSS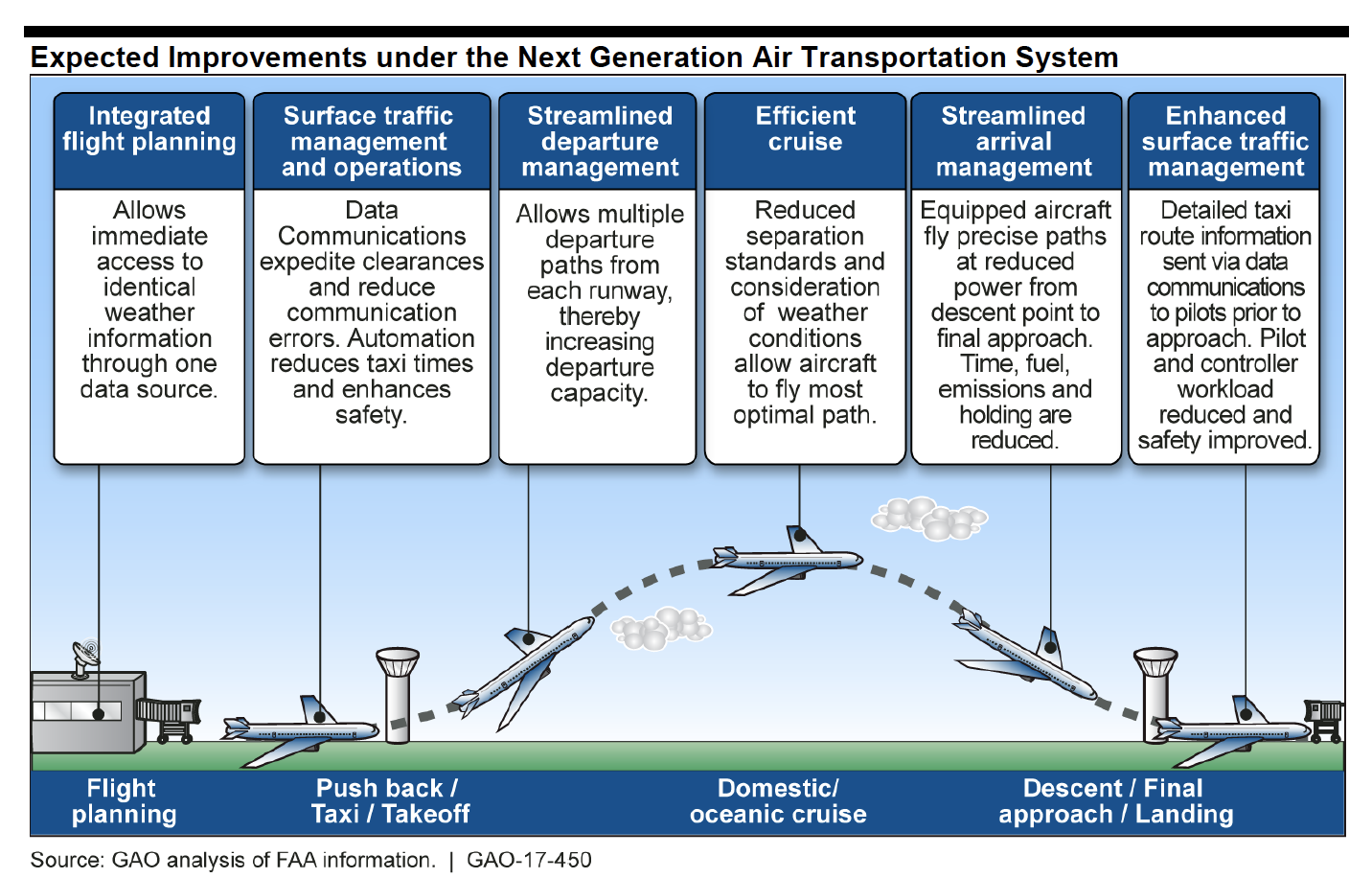
Improvements to the nation’s air traffic control system, including a shift to more efficient GPS-based routing and GPS-enabled aircraft surveillance, are largely on track and within budget, according to a recent watchdog report from the Government Accountability Office (GAO).
By Dee Ann Divis