Design Drivers and New Trends for Navigation Message Authentication Schemes for GNSS Systems
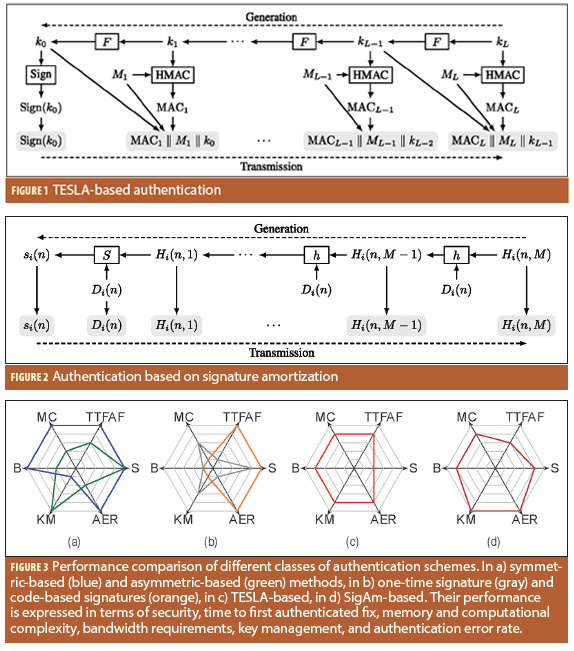 Figures 1-3
Figures 1-3Working Papers explore the technical and scientific themes that underpin GNSS programs and applications. This regular column is coordinated by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Günter Hein, head of Europe’s Galileo Operations and Evolution.
By Günter W. Hein