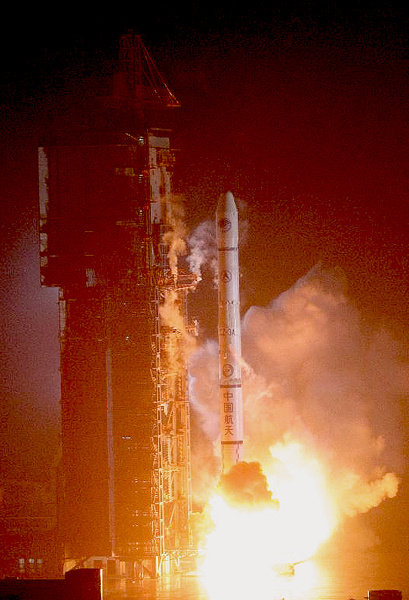
Launch of GPS Block IIR-M satellite, October 17, 2007
Launch of GPS Block IIR-M satellite, October 17, 2007A Block IIR-M GPS satellite was launched successfully today (October 17, 2007) from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. Expected to be set healthy for use in early November 2007, the spacecraft will be designated as PRN15/SVN55, referring to its pseudorandom noise code and space vehicle number, respectively.
A Block IIR-M GPS satellite was launched successfully today (October 17, 2007) from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. Expected to be set healthy for use in early November 2007, the spacecraft will be designated as PRN15/SVN55, referring to its pseudorandom noise code and space vehicle number, respectively.
The GPS IIR-17(M) satellite is the fourth in the GPS IIR series modernized with the new military code (M-code) and second civil signal (L2C). Currently 12 IIR and 4 IIR-M satellites are on orbit. It will be maneuvered into the F2 slot in the sixth of the six GPS orbital planes, near to a 16-year-old Block IIA space vehicle (SV29, PRN29) on which three of the satellite’s four atomic clocks have ceased functioning.
The GPS IIR-17(M) satellite, built by Lockheed Martin and launched aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket, joins the GPS constellation of 30 operational satellites. The GPS IIR-M satellites features include two new military signals for improved accuracy, enhanced encryption, anti-jamming capabilities, and a second civil signal to provide dual frequency capability and improve resistance to interference.
The GPS IIR-M launch was also the first to be conducted with the new Launch and Early Orbit, Anomaly Resolution, and Disposal Operations (LADO) System for satellite command and control during launch. LADO will be replacing and will perform the same functions that are normally accomplished by the Command and Control System, according to the GPS Wing.
Once operational, the new GPS LADO system will allow cradle-to-grave operations for GPS under command by the 2nd Space Operations Squadron at the GPS Master Control Station, Schriever AFB, Colorado, and their Reserve associate unit the 19th Space Operations Squadron. LADO will relieve the GPS program of its dependence on CCS for spinning satellite operations. The system will also support existing GPS IIA/IIR/IIR-M satellites in the GPS operational constellation for all LADO mission functions, perform launch for remaining IIR-M satellites, and be used for on-orbit GPS test and check-out activities.
The next launches of GPS IIR-M satellites are scheduled for "no sooner than" December 2007 and March and June 2008.
The accompanying photo of the launch is courtesy of United Launch Alliance – Carleton Bailie.
Copyright 2007 Gibbons Media & Research LLC