Sony Corporation announced the upcoming release of GNSS receiver large-scale integrations (LSIs) for use in IoT and wearable devices. The new receiver LSIs offer low power consumption for dual-band positioning operation at 9 mW.
Increasing use of IoT and wearable devices that utilize location information has produced growing demand for GNSS receiver LSIs. Precise positioning and reliable communications must be ensured to maintain proper operation of IoT and wearable devices, which are being used even in difficult communication environments and unstable conditions, such as multipath propagation situations caused by reflection off the ground or nearby buildings or the effects of the swinging of the arms when attached to a person’s wrist. Additionally, device size constraints necessitate a compact battery, whereas satellite signal reception and positioning when using GNSS functionality typically consumes a lot of power, resulting in poor battery life.
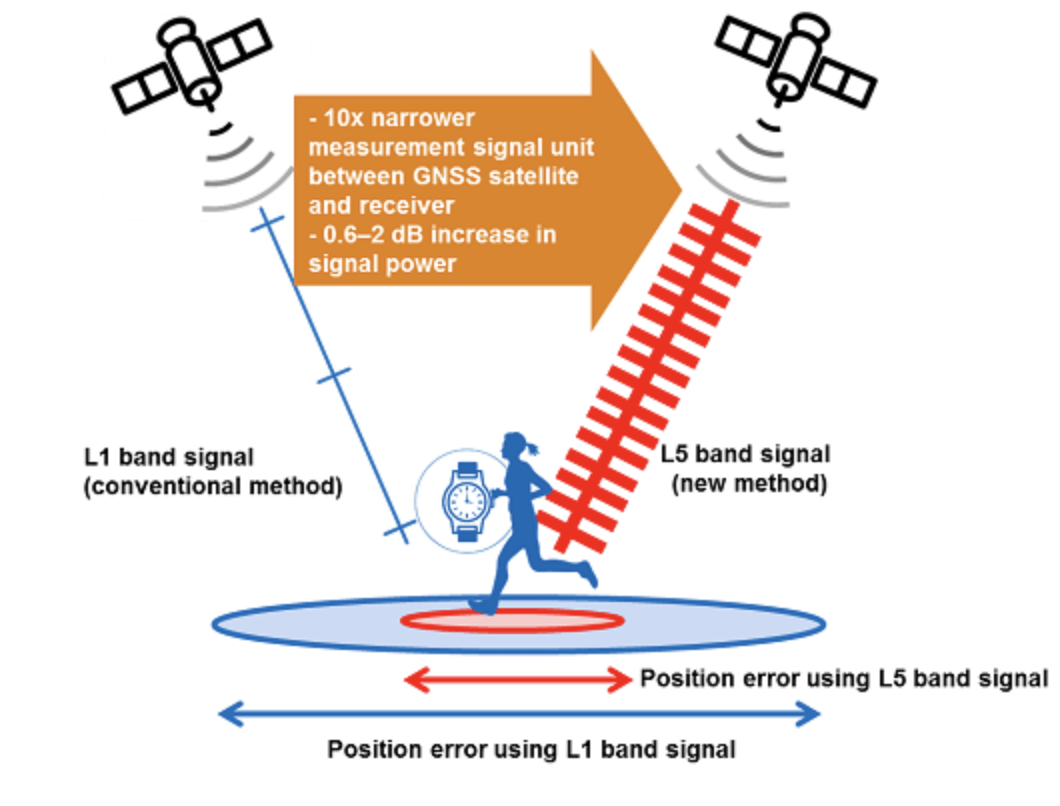
The new LSIs support L5 band reception as well as L1. L5 is currently being expanded across GNSS constellations, making them capable of dual-band positioning. Sony’s algorithms enable stable, high-precision positioning even under the difficult conditions unique to wearable devices. Also, the use of Sony’s high-frequency analog circuit technology and digital processing technology delivers low power consumption during continuous positioning for dual-band reception operation, at 9 mW.
The new LSIs will drive greater opportunities to develop new products and services such as smartwatches and other wearable devices that cannot use external power supplies, as well as IoT devices used for applications such as trackers. They also show promise in a wide variety of applications which require precise positioning and stable communications, such as automotive services.
L5 Advantages
Compared with the L1 band, the new signal method used in the L5 band employs signal units that are 10 times narrower to measure the range between the GNSS satellite and receiver, improving positioning precision and amplifying the transmission power from the satellite, resulting in high-precision, high-sensitivity positioning.
Quick, accurate GNSS signal reception via Sony’s algorithms enables positioning that is more stable even in changing reception environments, such as obstructing from buildings when on the move and acceleration of wearables due to swinging of the arms. This also leads to quick positioning time even from cold starts, which require more time. Additionally, Sony’s digital signal processing technology enables countermeasures against the performance degradation caused by radio interference from aircraft communications as well as spoofing attacks and other issues, thereby improving resistance to interference, according to the company.
Low power consumption and high sensitivity are delivered by Sony’s analog circuit technology, which enables low-voltage operation, as well as digital circuits and software algorithms that enable software processing via low clock frequencies.