The French company Geoflex demonstrated GNSS corrections-driven centimetric positioning in Brazzaville, Republic of Congo on July 8, at the national Stadium Alphonse Massamba-Debat. The demo employed a dual-frequency GNSS chipset receiving GPS and Galileo signals and the Geoflex corrections service via the Nigerian NIGCOMSAT-1R satellite on L Band, a frequency directly received by the chipset without any cellular connectivity.
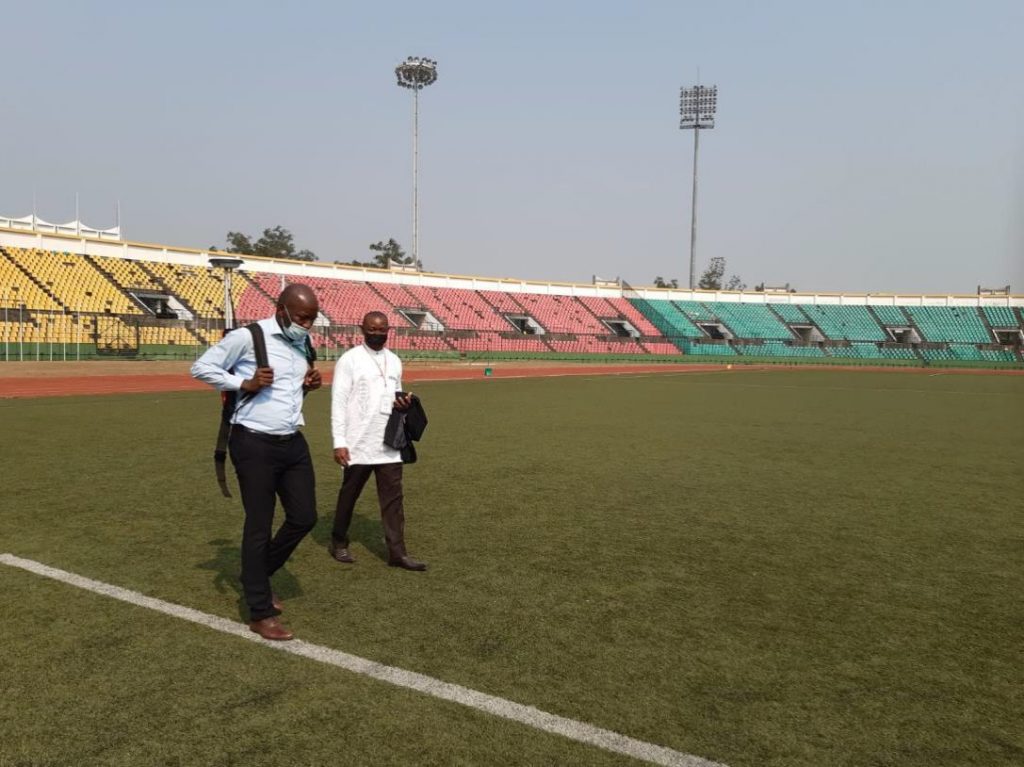

The Geoflex corrections increased the accuracy of the position from the GPS/Galileo chipset from 3-10 meters to centimetric level: 5 cm (East), 6.1 cm (North) and 14.4 cm (Up) with 68% confidence level. To show the improved accuracy, the demonstration device followed the marking of the football stadium.
This paves the way for precise applications across the African continent in a broad range of sectors, including precision agriculture, land and maritime transport, rail safety, drone navigation, mapping and surveying.
Geoflex’s hypergeolocation service has been available since 2018 as a subscription via the Internet, in real time or in post-processing. However, this demonstration of reception through the L Band of NIGCOMSAT-1R removes the need for an additional telecom link, allowing precise positioning wherever the satellite signal is broadcast: over Africa and Indian Ocean.
The demonstration was funded by Agence pour la Sécurité de la Navigation Aérienne en Afrique et à Madagascar (ASECNA), and technically developed in partnership with Thales Alenia Space, NIGCOMSAT and the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (ASECNA ().
The corrections technology was initially developed by the French space agency CNES in research spanning 12 years. It is protected by 7 patents licensed to Geoflex, which continues the co-development of the technology together with the CNES. In addition to its core data service, Geoflex has developed a positioning engine which includes sensor fusion with a large variety of other technologies: inertial, optical, communications, as well as a hardware development kit.
Geoflex provides universal hypergeolocation to a large number of use cases: trains, cars, vessels, drones, smartphones, robots, agriculture machinery and more. The European GNSS Agency estimates that the market addressed by Geoflex GNSS augmentations will grow from €23 Billion in 2020 to €42 Billion in 2025.
The Agency for Air Navigation Safety in Africa and Madagascar (ASECNA), Nigerian Communications Satellite Ltd. (NIGCOMSAT) and Thales Alenia Space, the joint venture between Thales (67%) and Leonardo (33%), are working together to accelerate the development of additional satellite services provided by ASECNA’s A-SBAS (Satellite-Based Augmentation System) for Africa and the Indian Ocean to deliver precise point positioning (PPP, CNES/Geoflex) and danger warnings for a wide range of applications in Africa.
The three partners have broadcast the SBAS signal over the Africa & Indian Ocean (AFI) region since September 2020 to provide the first SBAS open service in this part of the world via the NigComSat-1R satellite. This trial follows successful flight demonstrations in January 2021 in Lomé, Togo and the following June in Douala, Cameroon.
The first demonstration of the special urgent situation warning service via satellite showed the system’s ability to broadcast a warning message via the A-SBAS signal to mobile phones, without requiring a terrestrial network. This service sends a message to the populations concerned, providing information on the type of danger and instructions to be followed. The second demonstration entailed the transmission of GNSS corrections based on CNES/Geoflex PPP technology and also using the A-SBAS signal. This approach showed the system’s ability to achieve positioning accuracy to within centimeters across the entire African continent.
ASECNA is an international public organization. Its main mission is to provide air navigation services within an airspace of 16,500,000 square kilometers, divided into six flight information regions (F.I.R) as defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). ASECNA also develops solutions for airport management, aviation infrastructure studies and construction, equipment maintenance, calibration of air navigation instruments and training for civil aviation staff.
Nigerian Communications Satellite Ltd. (NIGCOMSAT) is a company and agency under the Federal Ministry of Communications and Digital Economy whose mission is to be the leading satellite operator and service provider in Africa. NIGCOMSAT Ltd. owns and operates the Nigerian communications satellite system. The company provides innovative and cutting-edge satellite communications solutions by operating and managing a geostationary communication satellite, NigComSat-1R, built to provide domestic and international satellite services via a 2-way satellite communications system across West, Central and Southeast Africa, as well as Europe and Asia. The satellite is a hybrid communication satellite with a payload for navigation overlay services (NOS) similar to EGNOS.





