The Position Authenticated Tachograph foR OSNMA Launch (PATROL) project is developing the first external GNSS facility for smart tachographs, using Galileo’s new Open Service Authentication (OS-NMA). The tachograph, a device fitted to a vehicle that automatically records its speed and distance, together with the driver’s activity selected from a choice of modes, uses Galileo authentication to verify that the navigation data received from satellites is genuine.
The user terminal is compliant with new European regulations for tracking. It provides trusted position and time using satellite navigation systems, acting as an external GNSS facility (EGF) for smart tachographs.
Since 2006, all European vehicles over 3.5 tonnes or transporting more than 9 persons must be fitted with a digital tachograph, to ensure the safety and working conditions of drivers. Digital tachographs provide enforcers with a witness of the drivers’ driving times, break and rest periods. The new 2019 regulations for Smart Tachographs require the use of GNSS for:
- The provisioning and recording of vehicle positions.
- The recording of the vehicle’s position declared by drivers at start / end of their daily work period.
- The automatic recording of the vehicle’s position, each time the accumulated driving time reaches 3h.
- Securing the speed provided by the motion sensor of the vehicle (to be corroborated by vehicle motion information derived from the GNSS receiver).
- Securing time.
- Triggering events (absence of position information from GNSS receiver, vehicle motion conflict, time conflict).
PATROL’s main objective is to deliver a robust position, navigation and time (PNT) solution, complemented by additional GNSS spoofing detection techniques and IT security features, in a user terminal, using commercial GNSS receivers. By this means it aims to:
- Develop a European GNSS validation platform to test GNSS receivers against emerging threats.
- Assess GNSS vulnerabilities, with and without OS-NMA service.
- Implement state of the art GNSS threat mitigation strategies, complementary to OS-NMA.
- Facilitate the adoption of OS-NMA in the tachograph industry and other markets.
Additionally, the project produces draft guidelines for the implementation of OS-NMA in receivers, obtained from an extensive performance assessment campaign.
User terminal

The User Terminal includes a dual-frequency L1 and L5 Galileo and GPS board, a module for the use of Galileo OS-NMA, Sensor Fusion, a Centralized Authentication Management (CAM) software, tamper detection technologies, advanced GNSS spoofing mitigation techniques. The User Terminal features are complemented with a set of tools able to emulate a Smart Tachograph, provide CAN BUS interface, generate synthetic CAN data for simulation purposes and interface to the GNSS Board for configuration and loading of the OS-NMA keys.

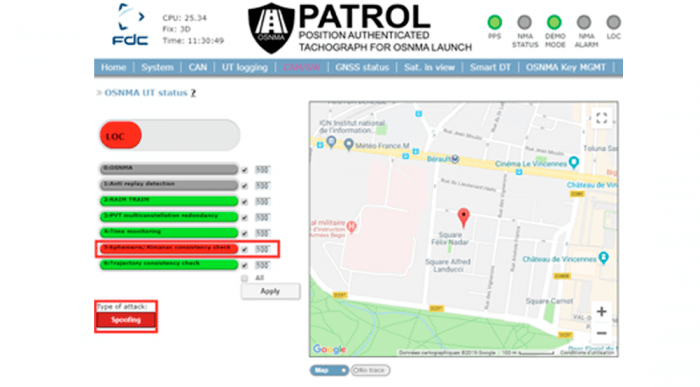
To complement OS-NMA, a number of anti-spoofing mechanisms are implemented, including:
- Chipset based anti-spoofing: AGC monitoring, CN0 monitoring, Signal Quality monitoring, Code-carrier consistency checking, OSNMA implementation, unpredictability-based SCER detection, Machine Learning Anti-spoofing, SBAS Data Checks, RAIM and Time RAIM, Position and Time Multi-constellation Redundancy Check
- Application based anti-spoofing: Time Monitoring, Ephemeris monitoring, Almanac monitoring, Tracked satellites monitoring, TTFF monitoring, Integration with external sensors (odometer, accelerometer, gyrometer)
A Validation Platform (VP) allows the end-to-end testing of the user terminal, supporting simulation of GNSS signals and advanced spoofing attacks, generation of OS-NMA data, modelling of user environments. It is installed in the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission in ISPRA, and leverages some of the tools already existing there. The Validation Platform measures the User Terminal performances against a number of key performance indicators. In future, it can be enhanced for the test campaign of several applications that need to validate Galileo Open Service Authentication. The Validation Platform enables both simulated and real-field environments, and provides automated tools for the generation of test results.
The Validation Platform is designed to stress the capabilities of the User Terminal under different real and simulated conditions.
Patrol team
The project is funded by the European GNSS Agency (GSA), with team players Qascom, FDC, ST Microelectronics, GMV aerospace and Defence, Actia and the University of Padova.