Return to main article: "Winging It"
GNSS technology is used in various ways to find attitude or trajectory. The simplest method relies on measuring the velocity of a single receiver and interpreting the direction of that vector as the vehicle’s heading.
This works for applications where a vehicle’s motion is constrained to only one axis – either absolutely, as with a train, or in the typical case of a car — when being driven responsibly!
By Inside GNSS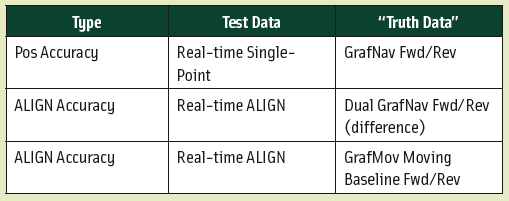
Return to main article: "Winging It"
With high-quality data sets obtained in the foot-to-foot configuration, we set about on postprocessing the data to extract more information about the NovAtel wingsuit system’s performance in the free-fall environment.
This was a multi-step process involving several NovAtel utilities and techniques, which we will describe here.
By Inside GNSS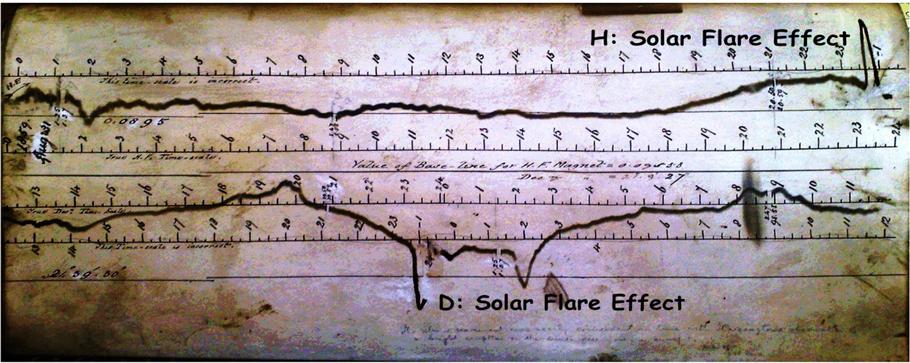 One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859
One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859 1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
 Nouméa ground station after the flood
Nouméa ground station after the flood A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat
A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
 Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated)
Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated) “Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto
“Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.
The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.  Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram
Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
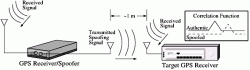
1. ICE BREAKER
Nome, Alaska USA
√ Two 2 1/2 pound GPS-guided UAVs that tolerate extreme cold helped bring fuel to snowbound Nome, Alaska over two weeks in January. On daily photographic missions, the Aeryon Scouts helped University of Fairbanks researchers map ice thickness in the frozen harbor so a Coast Guard icebreaker could slowly guide a Russian fuel tanker close enough to pump the fuel to shore.
Why Washington continues to talk about deficits while the country is talking about jobs and foreclosures is kind of a mystery, but let’s play along.
Following the failure of Congress’s would-be budget-cutting committee that wasn’t so super, the Department of Defense is facing about $500 billion in mandatory cuts over the next 10 years.
By Dee Ann Divis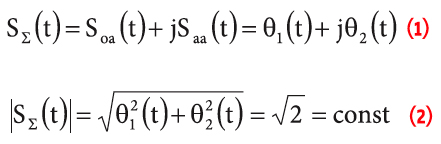
Working Papers explore the technical and scientific themes that underpin GNSS programs and applications. This regular column is coordinated by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Günter Hein, head of Europe’s Galileo Operations and Evolution.
By Inside GNSS FIGURE 2: Pseudorange computation based on transmission. On the left side, the satellites are transmitting mes¬sages synchronously. On the right side, the four subframes are received asynchronously, due to the different propagation time. The TLM word is taken as a referene. The time differences ?i are computed on the basis of the relative arrival times of the front of the first bit of the TLM word.
FIGURE 2: Pseudorange computation based on transmission. On the left side, the satellites are transmitting mes¬sages synchronously. On the right side, the four subframes are received asynchronously, due to the different propagation time. The TLM word is taken as a referene. The time differences ?i are computed on the basis of the relative arrival times of the front of the first bit of the TLM word.Q: How can pseudorange measurements be generated from code tracking?
A: Every GNSS receiver processes the received signals to obtain an estimate of the propagation time of the signal from the satellites to the receiver. These propagation times are then expressed in meters to solve for the user position using trilateration.
By Inside GNSS
Embracing the need for debt-driven discipline, the White House has revised its strategy for the nation’s defense, taking a more fiscally constrained approach that reduces the number of troops and future spending on defense systems.
The new plan, formally announced January 5, was already being put into effect last summer. “The strategic guidance was the compass by which we steered the budget review leading to the president’s budget for fiscal year ‘13 and the years thereafter,” Deputy Secretary of Defense Ashton B. Carter told reporters.
By Dee Ann Divis