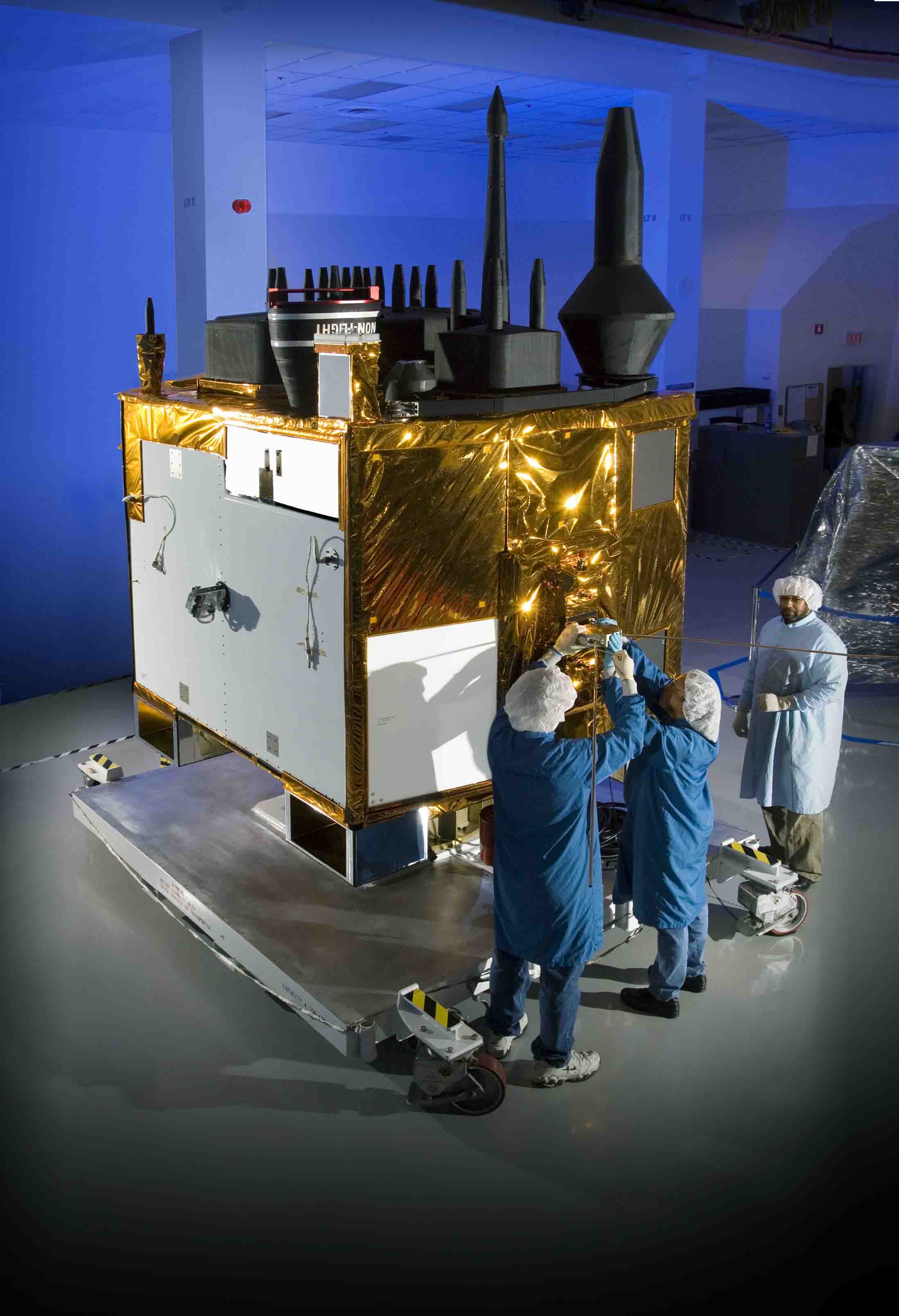
Air Force Investigating Residuals in GPS IIF Signals
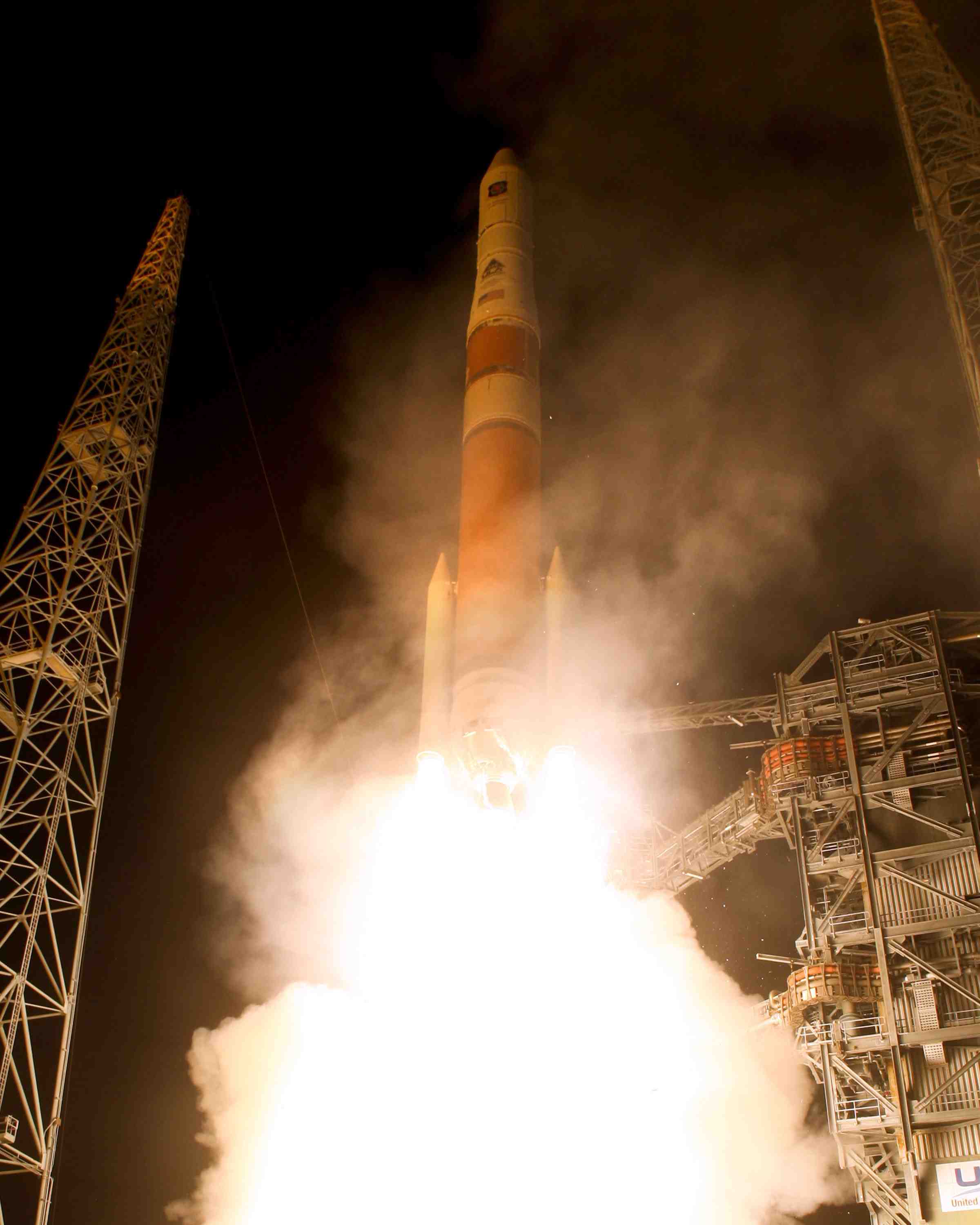 GPS IIF-SV1 launch. United Launch Alliance photo
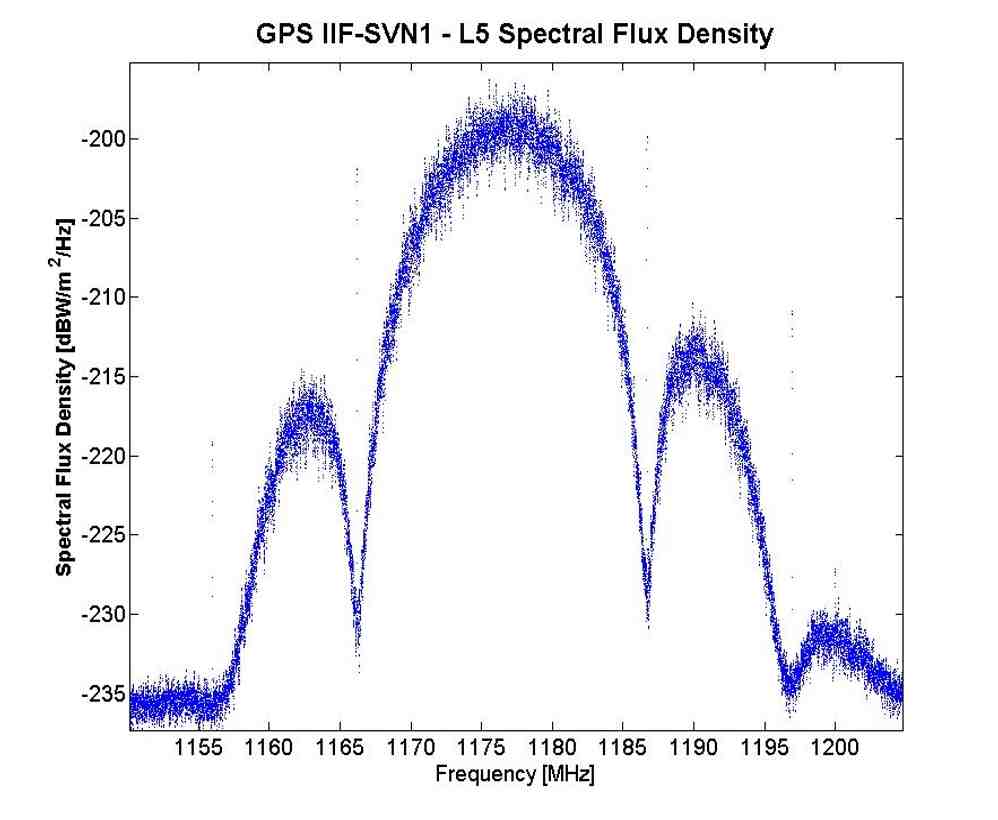
GPS IIF-SV1 launch. United Launch Alliance photo[Updated July 22, 2010] Air Force officials at the GPS Wing have confirmed that higher-the-expected range residuals detected by researchers at the German Aerospace Center (DLR) are appearing in signals transmitted by the first GPS IIF satellite, designated SVN/62/PRN25.
But the Air Force and Boeing Space and Intelligence Systems, which built the spacecraft, point out SVN62 is currently performing within specifications, and the signal phenomenon does not appear likely to have any significant effect on GPS positioning when the satellite is declared operational.
By Inside GNSS