Figure 2: GPS Interference Testing
Return to main article: "GPS Interference Testing"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "GPS Interference Testing"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "GPS Interference Testing"
By Inside GNSSThe gloves have come off now that test results show clearly the probable effects on GPS of LightSquared’s proposed wireless broadband network: widespread, debilitating interference to GPS receivers.
By Dee Ann Divis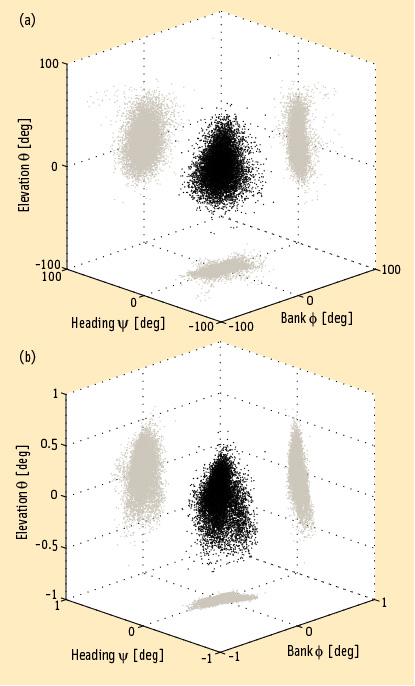 FIGURE 1: Heading, bank and elevation angles of an actual platform carrying two perpendicular two meter-long baselines. The attitude solutions are shown for both the derived, or float, measurements (top), as well as the carrier phase-based, or fixed, measurements obtained after having correctly resolved the integer ambiguities (bottom). Precision differs between the methods by two orders of magnitude. Gray dots represent the two-dimensional projections on each of the three coordinate planes.
FIGURE 1: Heading, bank and elevation angles of an actual platform carrying two perpendicular two meter-long baselines. The attitude solutions are shown for both the derived, or float, measurements (top), as well as the carrier phase-based, or fixed, measurements obtained after having correctly resolved the integer ambiguities (bottom). Precision differs between the methods by two orders of magnitude. Gray dots represent the two-dimensional projections on each of the three coordinate planes.Working Papers explore the technical and scientific themes that underpin GNSS programs and applications. This regular column is coordinated by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Günter Hein, head of Europe’s Galileo Operations and Evolution.
By Inside GNSSQ: What is a virtual reference station and how does it work?
A: To reach centimeter-level — or even better — accuracy of positioning typically requires use of precise dual-frequency carrier phase observations. Furthermore, these observations are usually processed using a differential GNSS (DGNSS) algorithm, such as real time kinematic (RTK) or post-processing (PP). Regardless of the specific differential algorithm, however, implicit in the process is an assumption that the quality of the reference station data is consistent with the desired level of positioning accuracy.
By Inside GNSS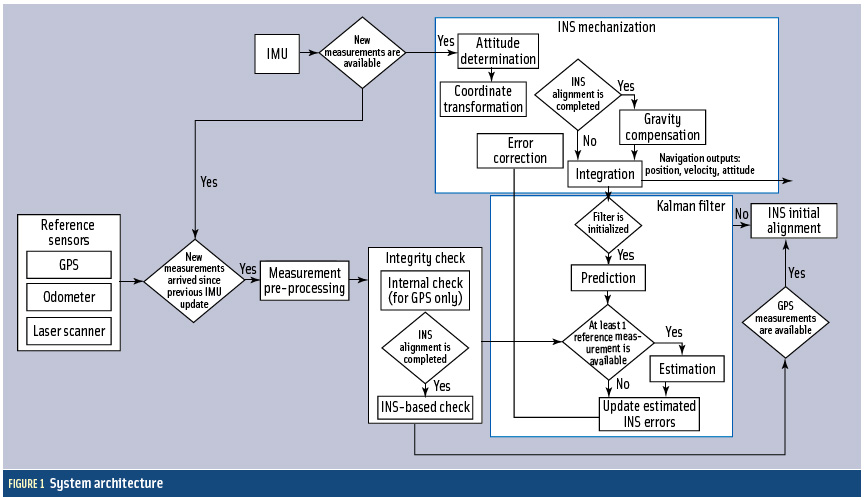 FIGURE 1: System architecture
FIGURE 1: System architectureCooperative vehicle safety applications should preferably have two-meter horizontal accuracy and six-meter vertical accuracy, all with a 95-percent availability. The solution must be developed to incorporate lower-cost sensor options, specifically, lower-cost inertial measurement units that can be generally characterized by the gyro drift of 100 degrees per hour and an accelerometer bias force of twice its mass times gravity (two milligals).
By Inside GNSS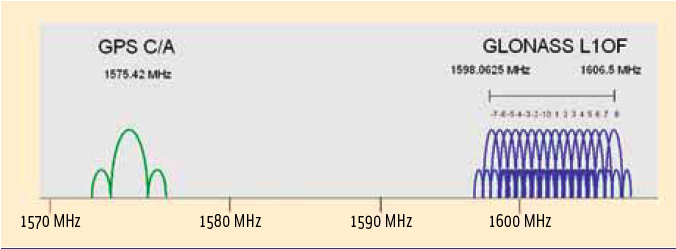 FIGURE 1: GPS/GLONASS L1 frequency band
FIGURE 1: GPS/GLONASS L1 frequency bandAs is well known, Galileo will become the European complement to the U.S. Global Positioning system.
But what about Russia’s GLONASS?
Although this constellation has been in operation for nearly three decades, the limited number of available satellites along with an uncertain governmental commitment to GLONASS performance until recent years had seriously restricted its use for aviation.
By Inside GNSSA GNSS signal simulator is mainly used to simulate GNSS signals transmitted by navigation satellites, propagated through the Earth’s atmosphere, and received by the receiver antenna. A simulator provides a convenient signal source for the test and validation of receiver function and performance and can also be used in GNSS experiments and studies of signal/data processing algorithms.
By Inside GNSS Anechoic chamber test site at U.S. Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) facility in Patuxent River, Maryland
Anechoic chamber test site at U.S. Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) facility in Patuxent River, MarylandInterference can pose a threat to the reception of GNSS signals in a variety of ways. Even low-level signals have the potential to interfere with GNSS receivers, which require very high sensitivity for acceptable performance due to the extremely low received GPS signal power at the Earth’s surface.
By Inside GNSSWashington View appears in each issue of Inside GNSS. It covers U.S. policy and program issues involving the Global Positioning System and other GNSSes. Reporting from Washington, D.C., columnist Dee Ann Divis has written about GNSS and the aerospace industry since the early 1990s in GPS World, Geo Info Systems, Jane’s International Defense Review, the Los Angeles Times, AeroSpace Daily and other publications.
By Dee Ann DivisReturn to main article: "Keeping the Spoofs Out"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Keeping the Spoofs Out"
By Inside GNSSReturn to main article: "Keeping the Spoofs Out"
By Inside GNSS