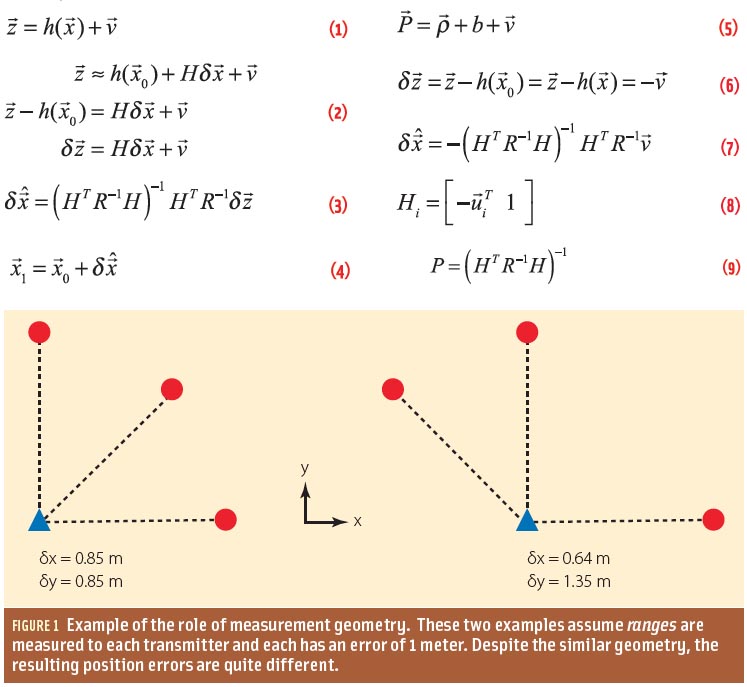
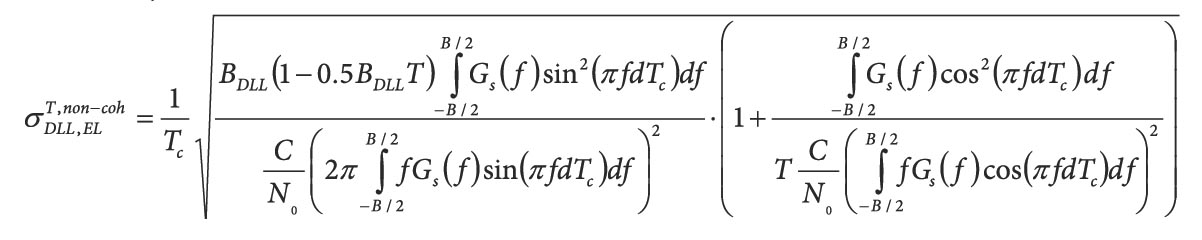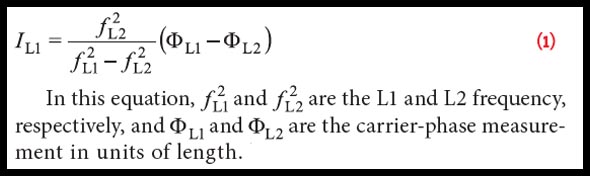GNSS & Geohazards
 Ken Hudnut, U.S. Geological Survey
Ken Hudnut, U.S. Geological SurveyFor at least two decades, GPS experts, geodesists, and public agencies have been working together to develop high-accuracy, large-scale continuously operating GPS reference stations that provide them the capability to monitor and model crustal deformation, tectonic plate movement, and the effects of geohazards such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Now, GNSS-augmented advance warning systems are going into place that can give us a crucial margin of safety in the event of an earthquake.
And none too soon.
By Inside GNSS