Successful launch of three Compass (Beidou-2) satellites so far this year and reports of another two planned later in 2010 have elevated awareness of China’s accelerating GNSS program.
Added to the two spacecraft placed in orbit in 2007 and 2009, that would bring the modernized Beidou constellation up to seven — halfway to the 13 or 14 satellites planned for the regional system scheduled to be available by 2012.
By Inside GNSS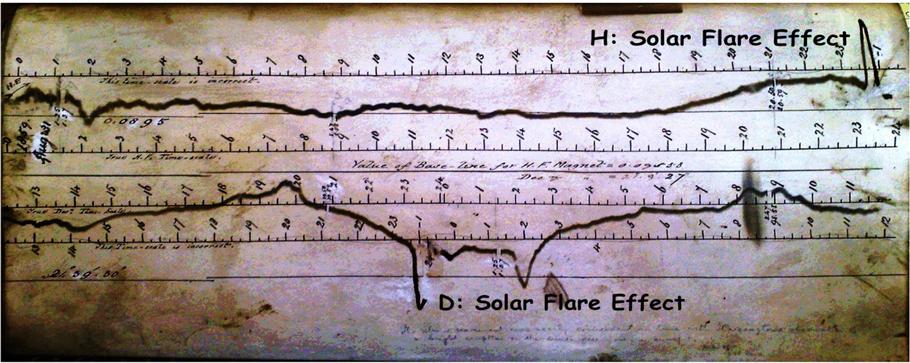 One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859
One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859 1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
 Nouméa ground station after the flood
Nouméa ground station after the flood A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat
A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
 Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated)
Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated) “Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto
“Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.
The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.  Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram
Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
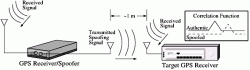
1. WHO WON?
Portland, Oregon and Munich, Germany
√ Judges all over the world are poring over 357 GNSS app innovations submitted to the 2010 European Satellite Navigation Contest from Europe, Australia, the Middle East, Taiwan and North America. Inside GNSS’s USA Challenge will announce our five finalists at ION GNSS 2010 in Portland, Oregon. The winners will celebrate on October 18 in Munich.

GPS-related procurement and development items in President Obama’s proposed budget for fiscal year 2011 are moving through Capitol Hill, but not without contention. At issue is Obama’s request for $40.9 million for the High-Integrity Global Position System (HIGPS, also known as iGPS).
By Inside GNSSIn recent years, researchers have explored possible new allocations for Radio Determination Satellite Service (RDSS) and Radio Navigation Satellite Service (RNSS) spectrum from a regulatory point of view. These studies have mainly discussed S-band and C-band in addition to L-band.
The International Telecommunications Union (ITU) Radio Regulations define RNSS as a subset of RDSS. Although the allocations are differentiated — RDSS usually has a paired uplink — both can actually be used for satellite navigation.
By Inside GNSSQ: Is it possible to define a fully digital state model for Kalman filtering?
A: The Kalman filter is a mathematical method, purpose of which is to process noisy measurements in order to obtain an estimate of some relevant parameters of a system. It represents a valuable tool in the GNSS area, with some of its main applications related to the computation of the user position/velocity/time (PVT) solution and to the integration of GNSS receivers with an inertial navigation system (INS) or other sensors.
By Inside GNSS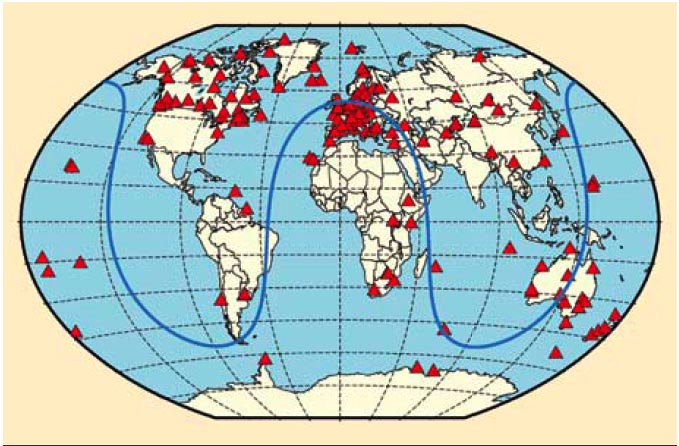 FIGURE 1: Geographical overview of the 170 IGS stations tracking SVN62/PRN25 during its current 90-day checkout period. The blue curve illustrates the ground track of the spacecraft on August 9, 2010.
FIGURE 1: Geographical overview of the 170 IGS stations tracking SVN62/PRN25 during its current 90-day checkout period. The blue curve illustrates the ground track of the spacecraft on August 9, 2010.For the complete story, including figures, graphs, and images, please download the PDF of the article, above.
On May 27, 2010, the U.S. Air Force successfully launched the first satellite of the Block II “follow-on” (Block IIF) series, the fourth generation of GPS spacecraft that features more precise and powerful signals, an extended design life, and several other technical advances.
By Inside GNSS