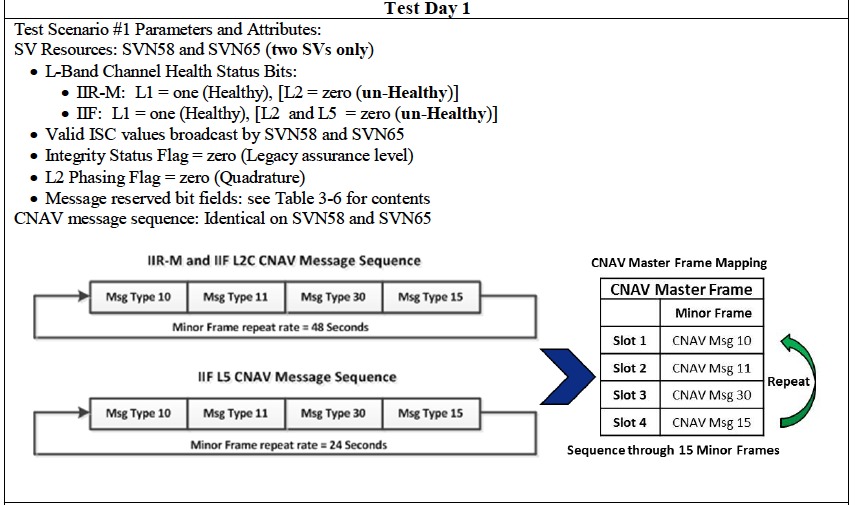
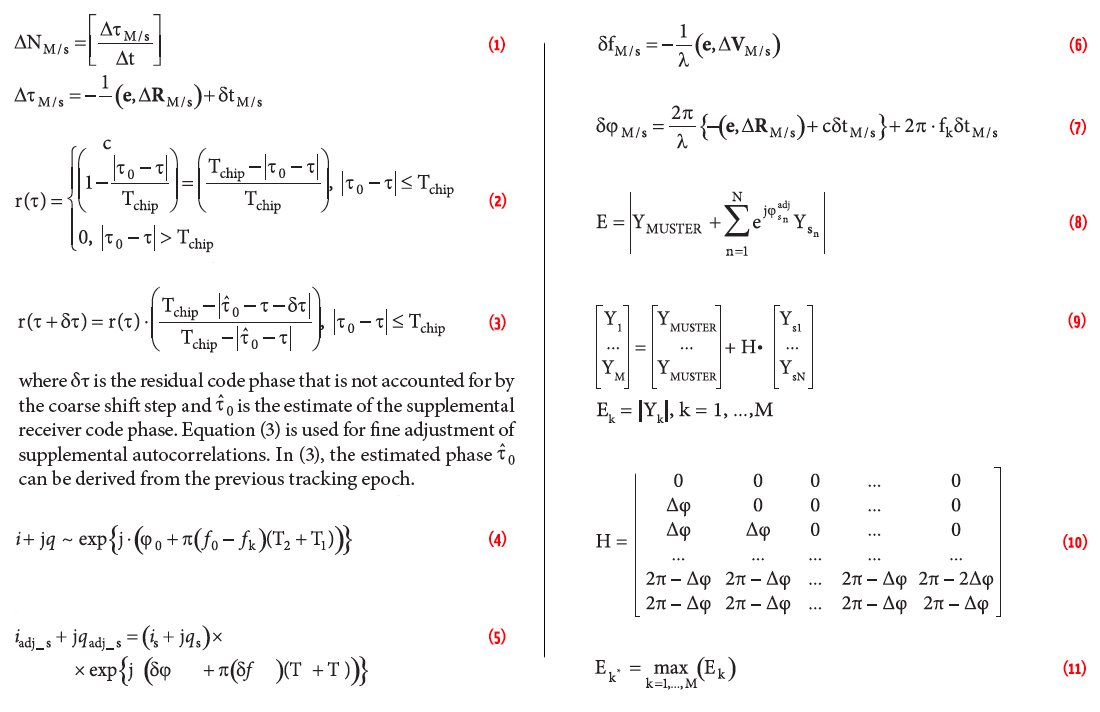
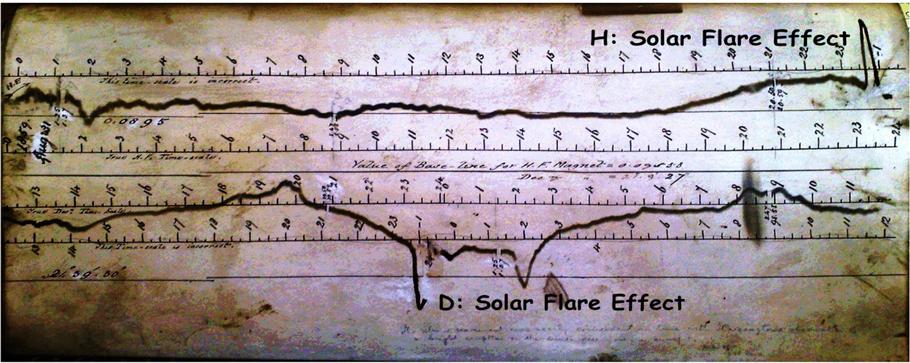
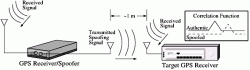
India Successfully Launches IRNSS-1A
 The IRNSS-1A spacecraft. ISRO photo
The IRNSS-1A spacecraft. ISRO photoIndia’s Space Research Organization (ISRO) reports that its first Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System satellite (IRNSS-1A), has reached geosynchronous orbit and all subsystems are operating normally.
The spacecraft was launched July 1 on board a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, PSLV-C22, from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota. This is the twenty third consecutively successful mission of PSLV.
By Inside GNSS