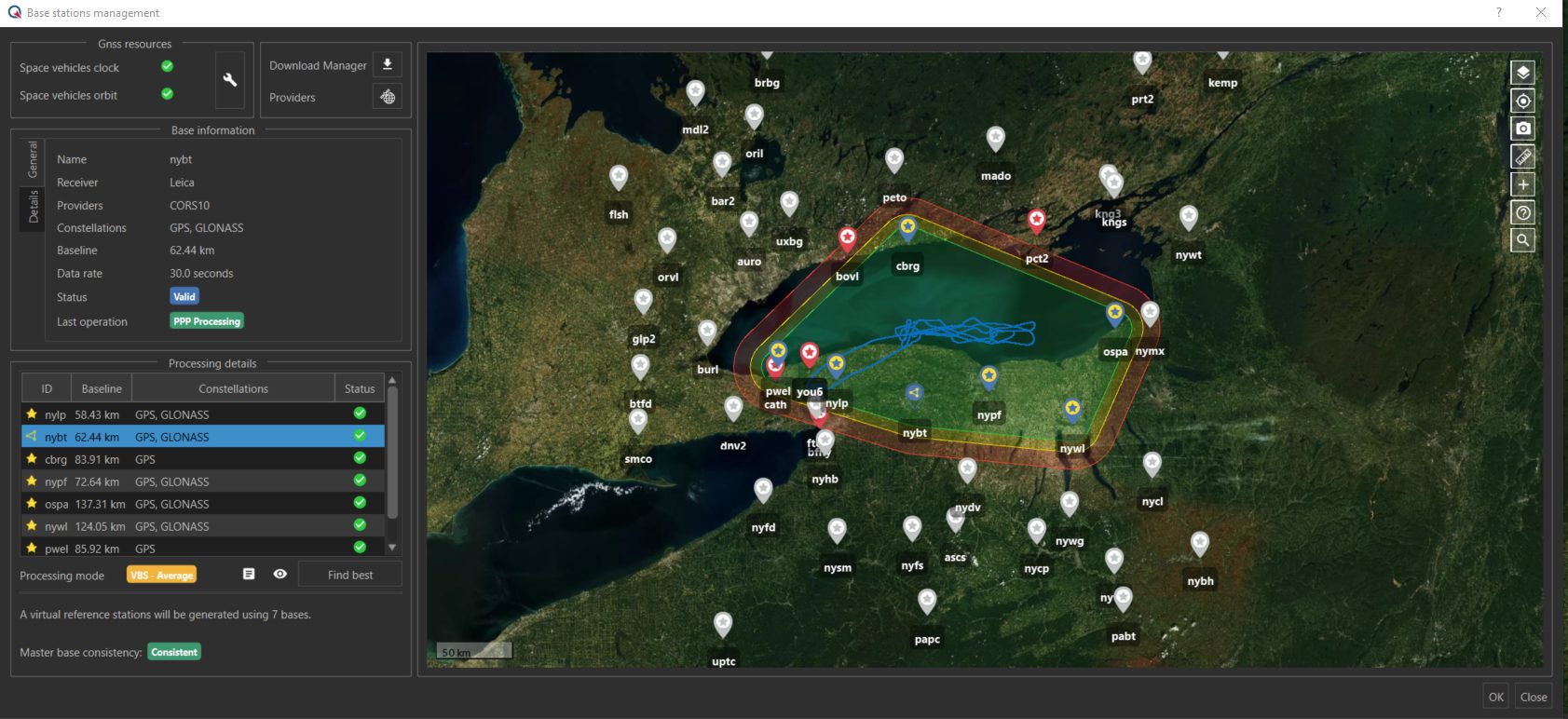
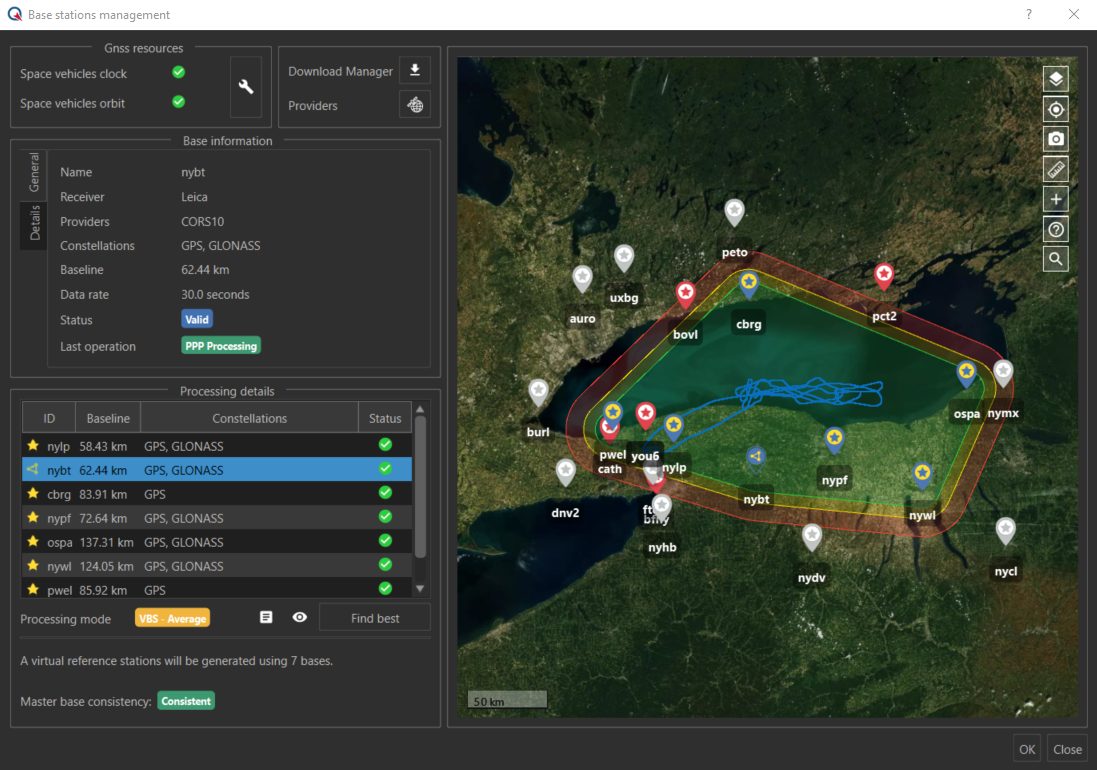
SBG Systems has released the Virtual Base Station feature in its in-house post-processing software called Qinertia. Geospatial professionals can benefit from an optimal centimeter-level position accuracy in all their projects, even for corridor mapping and in poorly covered RTK areas.
Qinertia is SBG Systems’ in-house GNSS and INS post-processing software. It gives access to offline RTK corrections from more than 7,000 base stations located in 164 countries. Trajectory and orientation are then greatly improved by processing inertial data and raw GNSS observables in forward and backward directions.
The solution maximizes corridor survey accuracy without compromise on processing time, according to the company. Its Qinertia PPK software now includes a new Virtual Base Stations (VBS) functionality. The VBS consists of computing a virtual network around a project in which position accuracy is maximized, homogeneous and robust, similar to a PPK short baseline. Surveyors can collect data far from base stations or over large areas, making it ideal for corridor mapping. After the mission, Qinertia chooses the most relevant reference stations, builds a virtual network, and brings the project to centimeter-level accuracy with no jump on accuracy nor convergence effects, even in urban areas.
Hardware Agnostic, Fast Processing
Qinertia has been designed to support all GNSS receivers and third-party inertial measurement units (IMUs). SBG Systems now offers a VBS that works any GNSS receivers from different brands, models, with different configurations or constellations, and even with different coordinate systems. Qinertia automatically adjusts the VBS network to compensate for any base station position inaccuracy and provides full quality control indicators to assess the expected accuracy and reliability. Qinertia VBS technology can mix users’ base stations with permanent network base stations to improve accuracy in remote locations. Qinertia processes quickly because it parallelizes the calculation of every base station in the virtual network and simultaneously processes the Forward and Backward computations. A typical UAV survey can be computed in less than a minute, according to the company.
Automatically Selects the Best Positioning; User Keeps Control
Qinertia is highly flexible and intelligent. It automatically selects the best positioning technology that applies to a user project, whether it is a single base station mode, the Virtual Base Stations mode, or a Precise Point Positioning computation. Control remains in the user’s hands, to manually choose the mode, take a base station away and add a new one, while Qinertia automatically re-checks and re-computes all parameters simultaneously to validate the accuracy and consistency. The user is invited to check every step and can consult various quality control indicators such as separation, standard deviation, bias, scale factor, lever arm, as well as export statistics reports (RMS, min/max).
For a demonstration video, click here.