The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has reported that the second inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO) satellite in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) has reached its intended orbital location and is operating normally.
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has reported that the second inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO) satellite in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) has reached its intended orbital location and is operating normally.
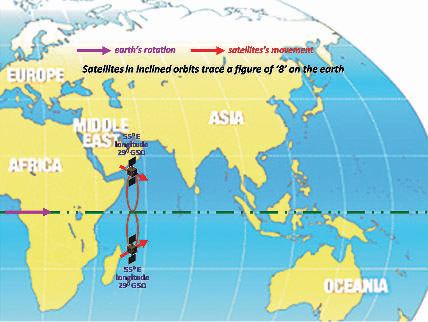
On April 23, 2014, ISRO announced that the IRNSS-1B had arrived at 55º East longitude, collocated with IRNSS-1A and the GSAT-8 spacecraft, which contains the GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) payload. IRNSS-1B was launched on board India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) from the Satish Dhawan Space Center on April 4.
The first satellite in the planned seven-satellite constellation, IRNSS-1A, was put into orbit last July.
Four satellites are enough to begin services, according to ISRO, and two more satellites are proposed for launch later this year.
The IRNSS is being developed in parallel with the GAGAN program, a satellite-based augmentation system similar to Europe’s EGNOS and the U.S. WAAS.
IRNSS will provide two types of service: Standard Positioning Service, open to all users, with an accuracy of 20 meters in the primary service area; and Restricted Service, which employs an encrypted signal accessible only to authorized users.The ISRO Navigation Center in Byalalu provides the navigation parameters, while the satellite is operated from ISRO’s Spacecraft Control Facility.






