 IP Solutions ReGen software simulator GUI
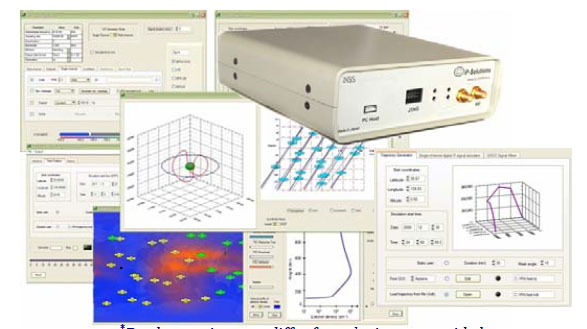
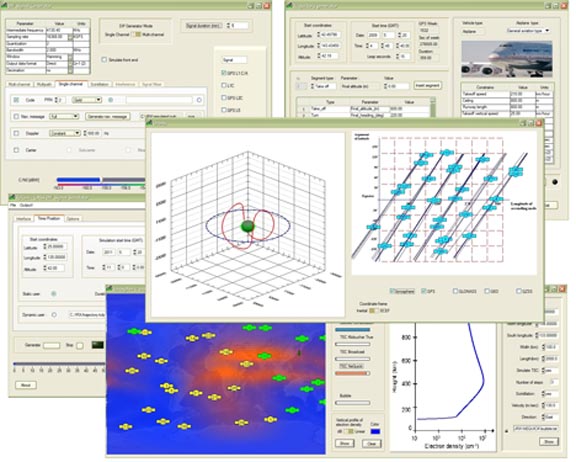
IP Solutions ReGen software simulator GUITokyo, Japan–based IP Solutions has released its ReGen GNSS DIF Signal Simulator, a software simulator that simulates ionospheric effects, generates digital IF (DIF) signals similar to those recorded by an RF recorder, and comes with an optional capability of simulating integrated inertial navigation.
Various configurations can produce multichannel GPS and GLONASS L1 signals and single-channel GPS L1, L2, L5 and GLONASS L1 and L2 signals, as well as simulating noise and interference.
Tokyo, Japan–based IP Solutions has released its ReGen GNSS DIF Signal Simulator, a software simulator that simulates ionospheric effects, generates digital IF (DIF) signals similar to those recorded by an RF recorder, and comes with an optional capability of simulating integrated inertial navigation.
Various configurations can produce multichannel GPS and GLONASS L1 signals and single-channel GPS L1, L2, L5 and GLONASS L1 and L2 signals, as well as simulating noise and interference.
In simulating atmospheric effects, the ReGen simulator incorporates Klobuchar and NeQuick total electron count (TEC) models and provides a fully controllable environment, according to the company, which includes ionospheric and tropospheric errors, multipath errors, satellite clock and ephemeris errors, ionospheric scintillation (using recorded or simulated 50Hz scintillation data), spatial errors, and navigation messages.
The simulator allows the addition of a simulated interference signal to recorded live signal and a GNSS receiver’s output in RINEX format.
Simulated or recorded DIF signals can be played back with IP Solutions’ Replicator, which streams the DIF signal into a J-type front end for real-time processing in a user’s software receiver or the signal can be fed into a user receiver baseband processor.
The INS add-on simulates INS output for a generated trajectory that can be used to facilitate R&D related to tight INS/GNSS coupling.
The ReGen DIF simulator was developed for JAXA, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency. It has also being purchased by INPE and IAE (Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais and Instituto de Aeronaútica e Espaço) — two of the leading aerospace research and development organizations in Brazil.
For further information, visit the company’s website.