ESA Signs Galileo IOV Launch, FOC Satellite Contracts
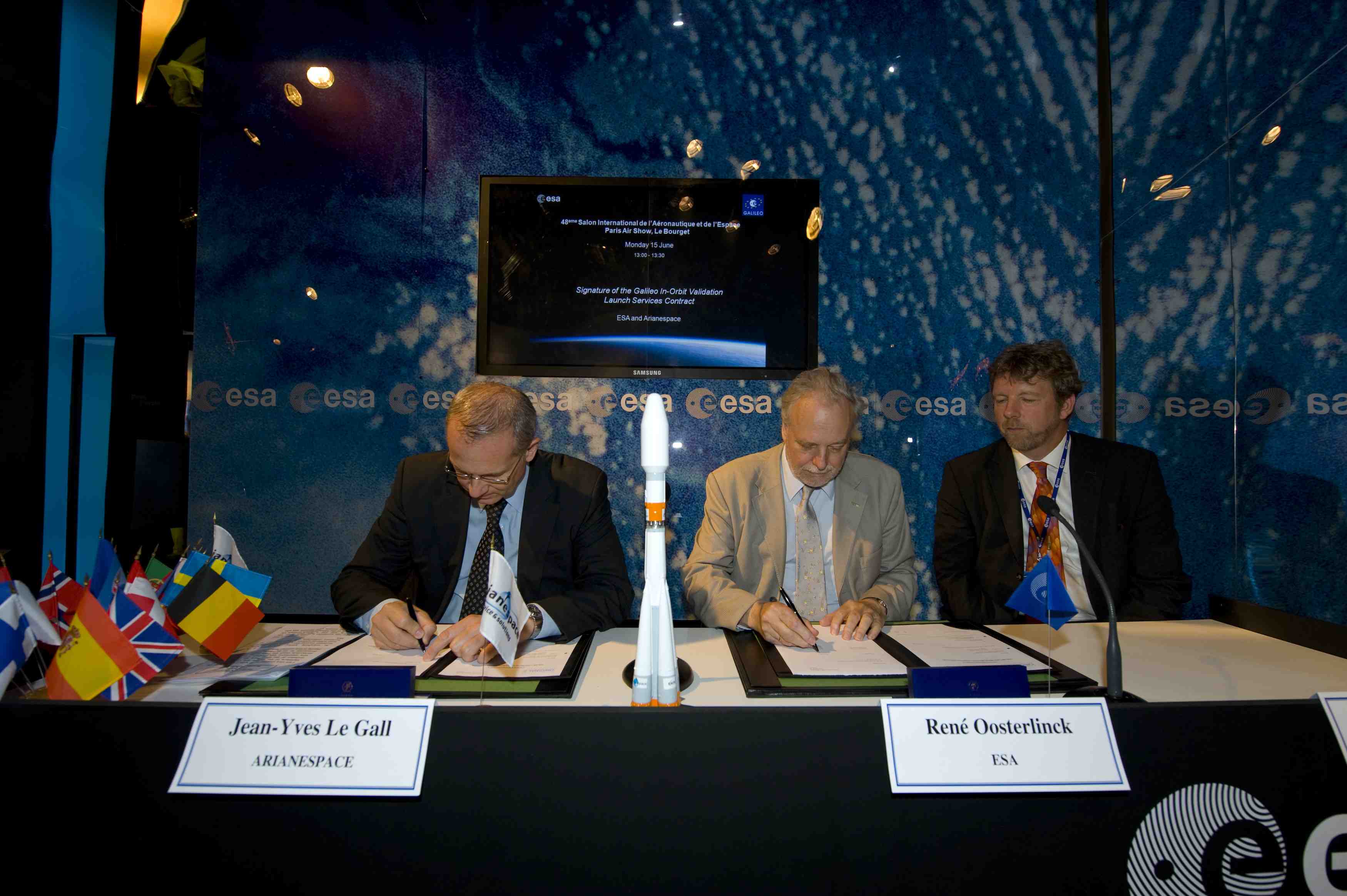 René Oosterlinck, ESA director of the Galileo Program and Navigation-related Activities (center), and Jean-Yves Le Gall, chairman and CEO Arianespace (left), sign the Galileo In-Orbit Validation Launch Services Contract in the ESA Pavilion at the Paris Air Show, Le Bourget. Paul Verhoef, programme manager of EU Satellite Navigation Programs at the European Commission. ESA photo — S. Corvaja, 2009
René Oosterlinck, ESA director of the Galileo Program and Navigation-related Activities (center), and Jean-Yves Le Gall, chairman and CEO Arianespace (left), sign the Galileo In-Orbit Validation Launch Services Contract in the ESA Pavilion at the Paris Air Show, Le Bourget. Paul Verhoef, programme manager of EU Satellite Navigation Programs at the European Commission. ESA photo — S. Corvaja, 2009On June 15, the European Space Agency (ESA) signed contracts for launch services on the Galileo in-orbit validation (IOV) satellites as well as two additional contracts for “long lead items” needed to build the full operational capability (FOC) Galileo constellation of satellites.
The first contract, with Arianespace, will provide launch services for the four IOV Galileo satellites that will be placed in orbit by the end of 2010. Two Soyuz rockets, each carrying two Galileo spacecraft, will launch from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.
By Inside GNSS