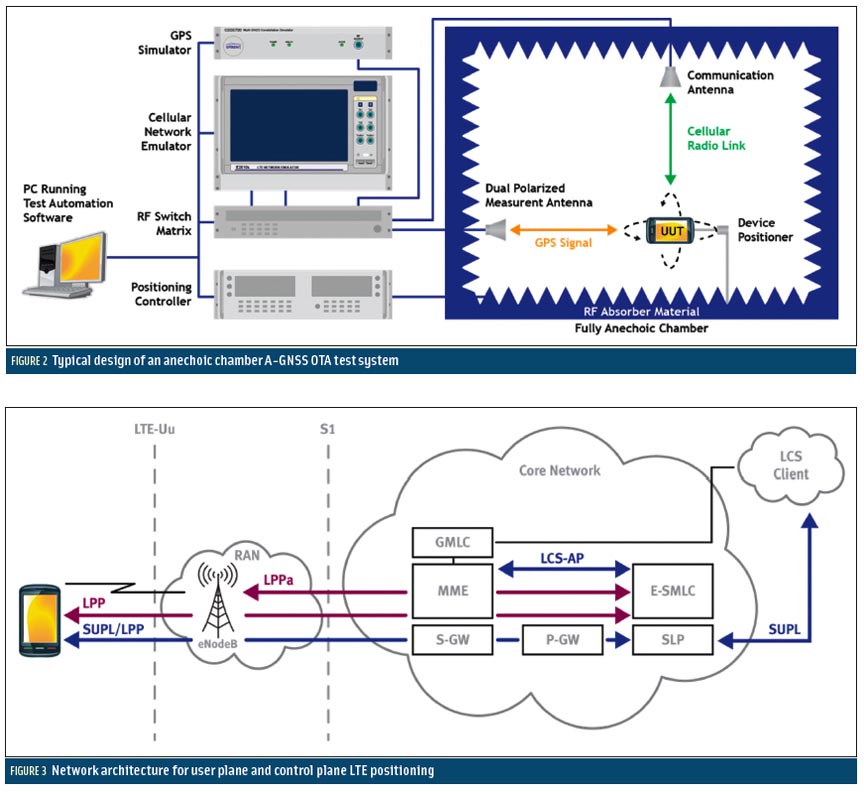
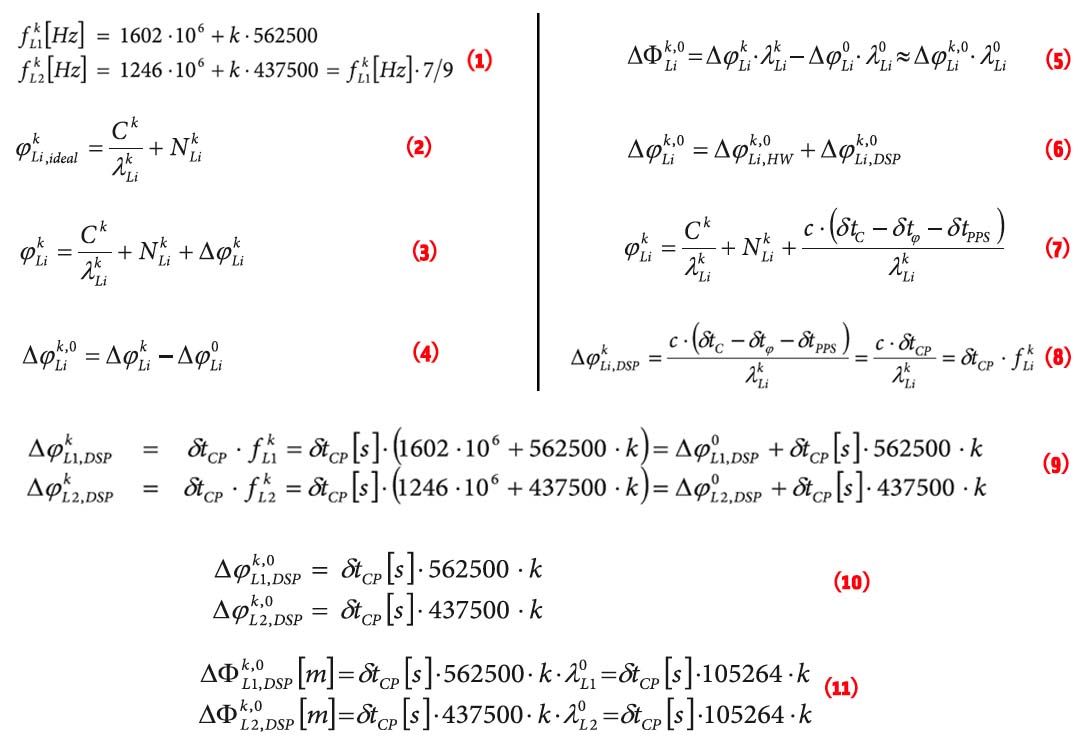
Developing a GNSS Position and Timing Authentication Testbed
 FIGURE 1: Characterization of interference from the user perspective
FIGURE 1: Characterization of interference from the user perspectiveIncreasing demand for ensuring the authenticity of satellite signals and position/velocity/time (PVT) calculations raises the need for tools capable of assessing and testing innovative solutions for verifying GNSS signals and PVT. Today’s civilian systems do not provide authentication at the system level, and a number of mitigation strategies have been developed in the last 10 years at user segment in order to protect receivers from interference and deception.
By Inside GNSS