Challenges of Ray-Tracing for GNSS Applications
Q: What are the challenges of ray-tracing for GNSS applications?
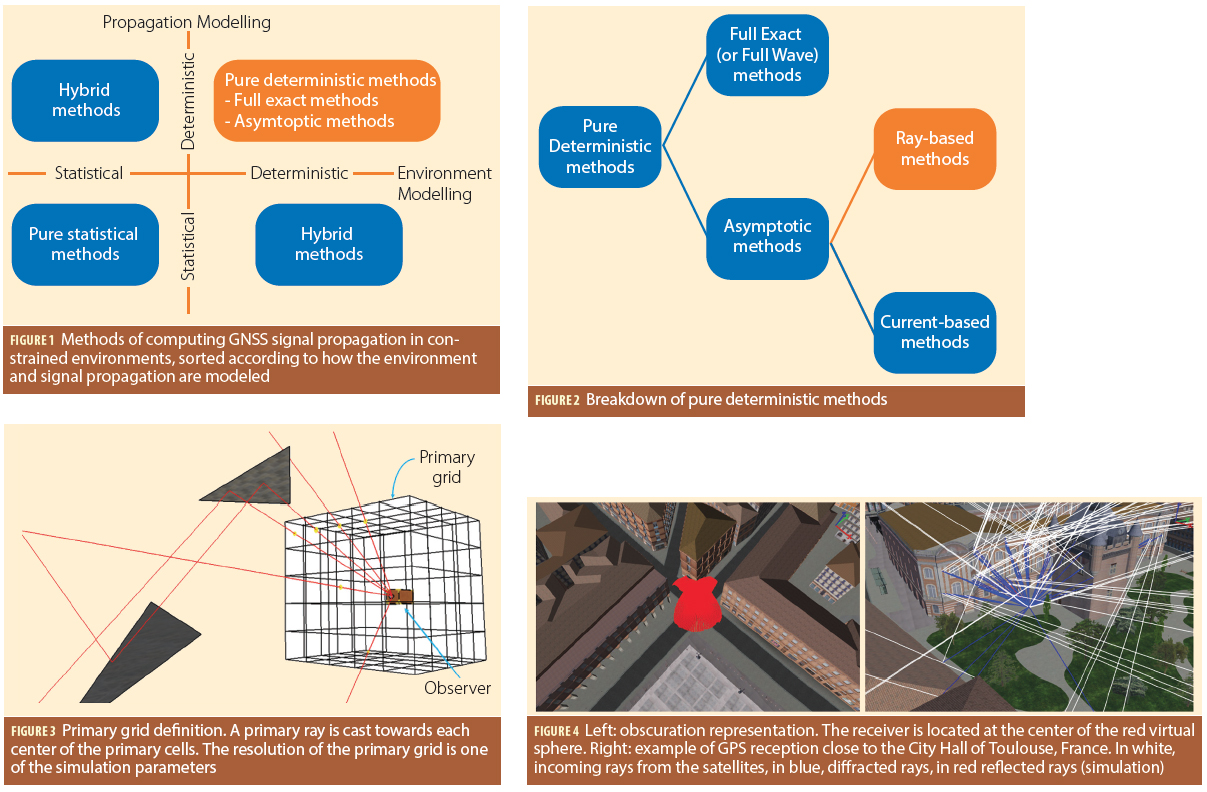
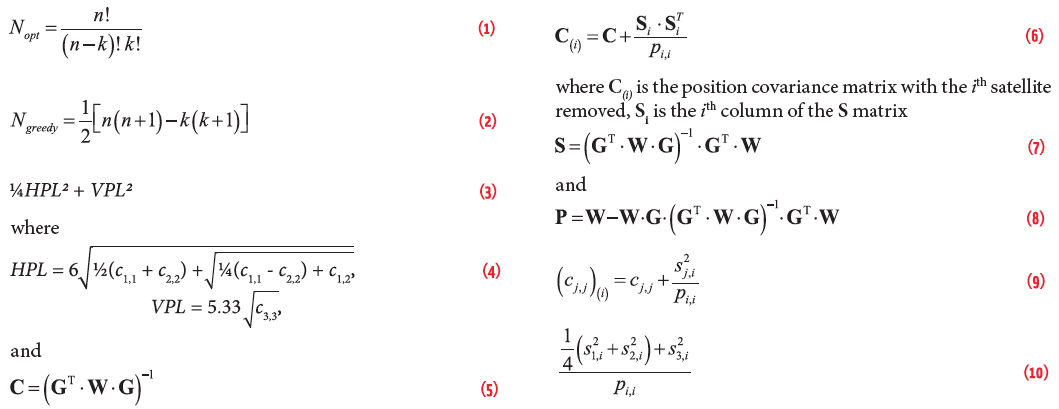
A: Simulating the propagation and reception of GNSS signals in complex environments is a challenging task. Indeed, the user always has to trade off between the computation time and the reliability of the output. Moreover, the motion of GNSS satellites, atmospheric effects, and building geometry are always difficult to model.
By Inside GNSS