Raytheon GPS Receiver Team Tracks M-Code Satellite Signal

The GPS Wing has announced that the Raytheon Modernized User Equipment (MUE) team has achieved live satellite M-code tracking with an MUE receiver.
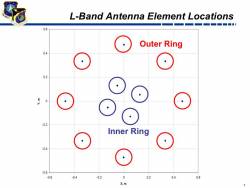
The team has developed modernized versions of the Avionics GPS Receiver Application Module and Ground Based GPS Receiver Applications Module (GB-GRAM) receivers under MUE receiver development contracts awarded to three companies in June of 2006. M-code signals from Block IIR GPS satellites were acquired using a Raytheon GB-GRAM-M.
By Inside GNSS



 before launch.jpg)







