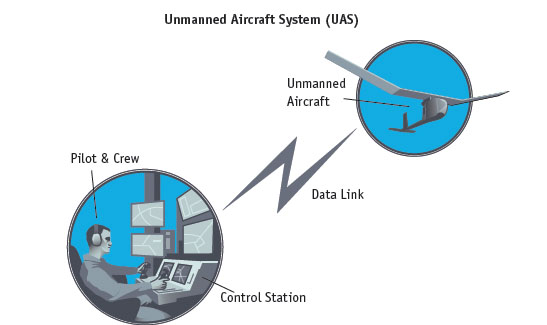
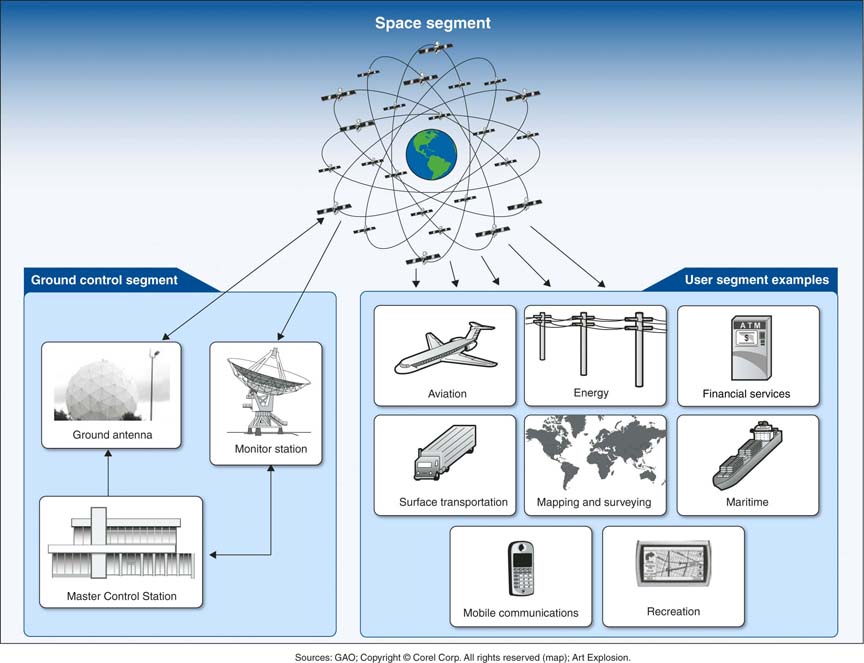
ION Pacific PNT Conference 2015

ION’s Pacific PNT Conference 2015 will take place April 20-23, 2015 at the Marriott Waikiki Beach in Honolulu, Hawaii.
The conference brings together policy and technical leaders from the Pacific Rim for policy updates, program status and technical exchanges on positioning, navigation and timing. The conference will include tutorials and a table-top exhibition.
Call for Abstracts will be available in Fall 2014. Registration will open in the Winter of 2014.
By Inside GNSS