The European Space Agency-funded DANGO project has developed a method for transforming Galileo high-accuracy service (HAS) signals for use in the Danish national reference frame (ETRS89DK).
Speaking at the recent final presentation of the DANGO project, DTU (Technical University of Denmark) Space Research Assistant Magdalena Golofit said, “HAS PPP corrections are delivered within the framework of the Galileo terrestrial reference system, GTRS, which is essentially equivalent to international terrestrial reference system, ITRS. What we wanted to do was to provide a direct, one-step transformation from the GTRS into the European terrestrial reference system for Denmark, which is ETRS89DK.”
The ETRS89 framework is a modification of the ITRS framework applied in Europe, balancing for continental drift in such a way that the total apparent angular momentum of continental plates is about 0.
“The two reference systems, ITRS and ETRS89DK, are not equivalent” Golofit said. “There is a position bias of approximately 70 cm, with the two positions diverging at a speed of about 2.5 cm per year.”
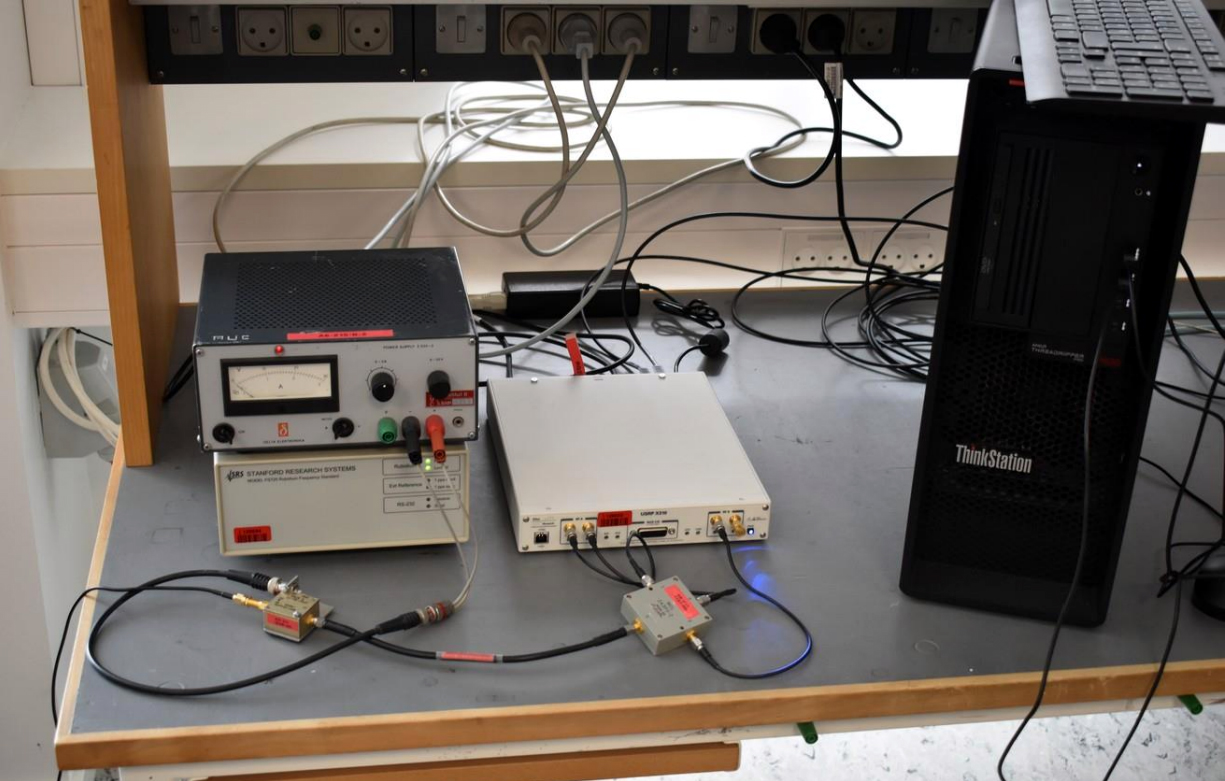
To derive the transformation, the team, which included researchers from DTU and Aalborg University (AAU), needed to determine appropriate Helmert transformation parameters. Seven parameters were eventually provided, calculated based on positioning data collected in 2024 at three continuously operating reference stations (CORS) established at DTU and AAU campuses. Equipment used included Septentrio PolaRx5s GNSS receivers with Leica LEIAR20 LEIM antennas.
Positive testing campaign
The collected data has been made accessible through the secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) data infrastructure. The stations will continue operating and be maintained by the universities.
DANGO results were validated using known positions of a national CORS network of 16 stations and using known positions of the TAPAS network. TAPAS is the Testbed in Aarhus for Precision Positioning and Autonomous Systems. The results evaluation compared residuals between known station coordinates in ETRS89DK and the coordinates transformed from ITRS into ETRS89DK.
HAS signals were extracted using a software defined receiver (SDR) data stream and a new HAS-capable GNSS receiver, the EOS Arrow Gold+.
In-situ tests were also performed comparing performance under different conditions: from a rooftop using a LEIAR20 LEIM antenna (ideal conditions); in urban conditions with an EOS antenna; in semi-urban conditions with an EOS antenna; and in kinematic tests with EOS antenna.
The project was part of ESA’s NAVISP Element 3 funding scheme, aimed at supporting national PNT strategies for the development and promotion of products, applications and services based on PNT systems.