India’s Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) provisionally certified the nation’s Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS) — the GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) system — to RNP0.1 (Required Navigation Performance, 0.1 Nautical Mile) service level on December 30, 2013.
India’s Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) provisionally certified the nation’s Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS) — the GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) system — to RNP0.1 (Required Navigation Performance, 0.1 Nautical Mile) service level on December 30, 2013.
The certification will enable aircraft fitted with SBAS equipment to use the GAGAN signal in space for en-route navigation and non-precision approaches without vertical guidance over Indian air space. India is the fourth country to offer safety of life, space-based satellite navigation services to the global aviation sector. The availability of GAGAN signals in space will bridge the gap between the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) and Japan’s MTSAT-based Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS) coverage areas, thereby contributing to seamless navigation across the regions.
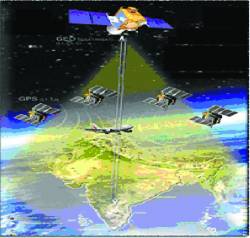
The GAGAN infrastructure includes 15 reference stations, three uplink stations, mission control centers, navigation payloads on two geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) transmitting GPS corrections in C and L bands, and associated software and communication links.
GAGAN’s service area includes India, the Bay of Bengal, South East Asia and the Middle East expanding up to Africa.
The GAGAN System, jointly developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Airports Authority of India (AAI) is scheduled for additional enhancement in the days to come, including the APV1/1.5 level of certification in the near future to offer precision approach services over the Indian land mass. The GAGAN signal is being broadcast through its GSAT8 and GSAT10 GEOs, covering the entire Indian Flight Information Region (FIR) and beyond. An on-orbit spare GAGAN transponder will be flown on GSAT-15.