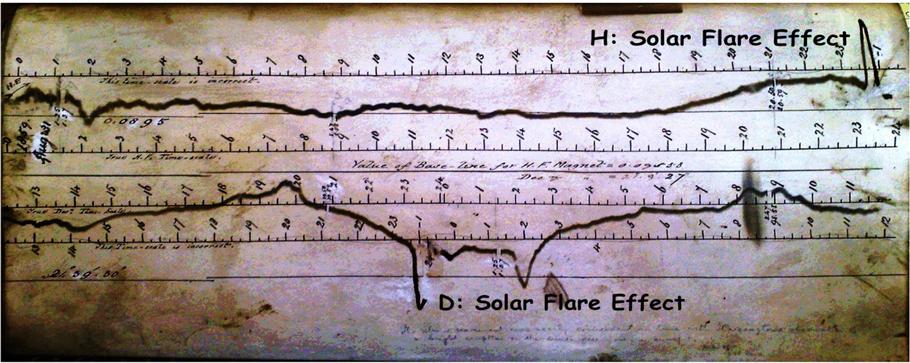
 One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859
One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859 1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
 Nouméa ground station after the flood
Nouméa ground station after the flood A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat
A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
 Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated)
Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated) “Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto
“Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.
The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.  Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram
Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
1. Mapping Air Traffic, Rainy Seasons, and More
Sahel, Africa
1. Mapping Air Traffic, Rainy Seasons, and More
Sahel, Africa
√ The European Space Agency (ESA) is using its Proba-V minisatellite to reveal – among other things – the seasonal changes in Africa’s sub-Saharan Sahel, with the rainy season allowing vegetation to blossom between February (top image) and September (bottom image). The semi-arid Sahel stretches more than 5,000 kilometers across Africa, from the Atlantic Ocean (Senegal, Mauritania) to the Red Sea (Sudan). The few months of the rainy season in the Sahel are much needed in these hot and sunny parts of Africa, and are critical for the food security and livelihood of their inhabitants.
Previously, the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and Luxembourg’s SES company added an experiment with Proba-V to detect Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast (ADS-B) aircraft signals from space. These signals are regularly broadcast from aircraft, giving flight information such as speed, position and altitude.
Described as ESA’s – and the world’s – first precision formation flying mission, Proba-3 is currently used for a wide array of missions.
2. Educating GNSS Students
Indian state of Telangana
√ The establishment of a new JNTU-Hyderabad GNSS lab is designed to provide an opportunity to the students, scholars and faculty members to carry out research in satellite-based navigation and to develop several advanced applications.
The Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University-Hyderabad (JNTU-H) and Hexagon Capability Centre India (HCCI) established the GNSS laboratory at the Centre for Spatial Information Technology, JNTU-H, according to recent reports from Telangana.
The lab is equipped with NovAtel GNSS receivers, antenna, systems, cables and other hardware components. The equipment enables reception, processing, analysis and development of navigational data and applications to augment curriculum for JNTU-H students for research and education. The university is located in Kukatpally, Hyderabad, in the Indian state of Telangana.
3. Flying Fruit
Eastern China
√ Chinese e-commerce giant Alibaba announced that it has used drones to deliver packages over water for the first time. Three unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) carrying six boxes of passionfruit with a combined weight of around 12 kilograms flew from Putian in China’s eastern Fujian Province to nearby Meizhou Island on October 31, the company said in a statement.
Flying into a strong wind, the drones took nine minutes to make the five-kilometer crossing. Each drone can carry up to seven kilograms, according to state-run Xinhua news agency. The drones were jointly developed by Alibaba’s delivery arm Cainiao Network, the company’s rural shopping platform Rural Taobao, and a domestic technology firm. According to Zeng Jinmei, an online store owner based on the island, the drone delivery service will cut the transportation time in half.
Alibaba plans to use drones to deliver high value-added products such as fresh food and medical supplies over water in the future.




