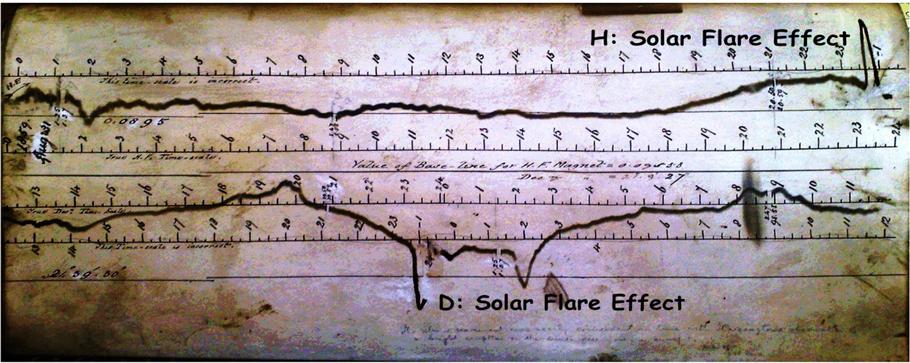
 One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859
One of 12 magnetograms recorded at Greenwich Observatory during the Great Geomagnetic Storm of 1859 1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
1996 soccer game in the Midwest, (Rick Dikeman image)
 Nouméa ground station after the flood
Nouméa ground station after the flood A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat
A pencil and a coffee cup show the size of NASA’s teeny tiny PhoneSat Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
Bonus Hotspot: Naro Tartaruga AUV
 Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated)
Pacific lamprey spawning (photo by Jeremy Monroe, Fresh Waters Illustrated) “Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto
“Return of the Bucentaurn to the Molo on Ascension Day”, by (Giovanni Antonio Canal) Canaletto The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.
The U.S. Naval Observatory Alternate Master Clock at 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever AFB in Colorado. This photo was taken in January, 2006 during the addition of a leap second. The USNO master clocks control GPS timing. They are accurate to within one second every 20 million years (Satellites are so picky! Humans, on the other hand, just want to know if we’re too late for lunch) USAF photo by A1C Jason Ridder.  Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram
Detail of Compass/ BeiDou2 system diagram Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
Hotspot 6: Beluga A300 600ST
1. FOLLOW THAT TRASH!
Seattle, Washington and Cambridge, Massachusetts
√ Trash/Track, a Seattle project created by MIT’s SENSEable City Lab, tracked a representative sample of city throwaways using GPS and CDMA cell-tower trilateration. Tagged items phoned home to an MIT server which mapped their progress in real time. Hint: Stuff doesn’t go away. http://senseable.mit.edu/trashtrack/
1. FOLLOW THAT TRASH!
Seattle, Washington and Cambridge, Massachusetts
√ Trash/Track, a Seattle project created by MIT’s SENSEable City Lab, tracked a representative sample of city throwaways using GPS and CDMA cell-tower trilateration. Tagged items phoned home to an MIT server which mapped their progress in real time. Hint: Stuff doesn’t go away. http://senseable.mit.edu/trashtrack/
2. SENSITIVE FOOTBALL
Pennsylvania USA
√ Was the football caught before it bounced? Did the quarterback make the goal? A Carnegie Mellon computer engineer and her students are using embedded touch sensors, GPS receivers and accelerometers to create a football that knows the answers. Their next prototype adds data from GPS receivers near the field. www.footballtracking.org/index.php
3. KOUROU STARTUP
Korou, French Guiana
√ Galileo is getting closer! A groundbreaking ceremony for Galileo’s central ground stations (TT&C, GSS, ULS) took place last November 19 inside CNES’s Centre Spatial Guyanais. The first two Galileo IOV satellites are expected to launch from CSG in November 2010 — but stay tuned for delays.
4. $500 MILLION!
London, United Kingdom
√ GNSS technology is everywhere — navigation, telematics, tracking, surveying machine control, and network timing– and shipment of its components and products will be worth 500 million in 2010, said ABI Research of London last December. And with multiple systems and related technologies, they expect $1.1 billion worldwide by 2014.
5. POWER SUPPLY
Lagos, Nigeria
√ Lagos state’s new Continuously Operating Reference Station must deliver real-time GNSS information . . . continuously. But Nigeria’s electrical grid is notoriously unreliable. Developer GeoQinetiq devised a system that channels public power through a low voltage monitor. During outages, it switches to daytime solar power or a backup charged by the other two sources.
6. IT’S ALIVE
GLONASS satellites
√ One of the three GLONASS-M satellites launched on December 14 went live on January 12. Looks like all is going well after schedule interruptions earlier caused by problems with a navigation payload on an in-orbit spacecraft. That brings the active satellite constellation to 21.



