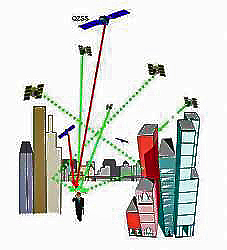
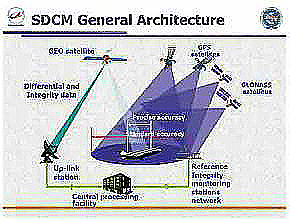
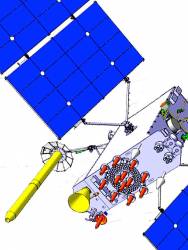
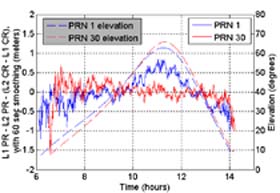
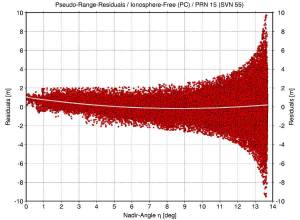
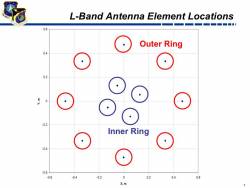
OCX budget Cut Could Slow Program; First IIF Might Launch by May 2010
An increasingly likely $97.4-million cut in the GPS OCX budget for fiscal year 2010 (FY10) would slow down work on modernization of the operational control segment, but the Air Force would try to recoup any reduction in the FY11 budget.
Meanwhile, technical problems that have delayed development of the follow-on generation of Block IIF satellites are largely resolved and a first launch is expected in May 2010.
By Inside GNSS