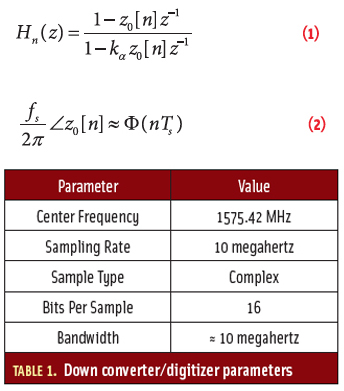
 Article Equations
Article EquationsWorking Papers explore the technical and scientific themes that underpin GNSS programs and applications. This regular column is coordinated by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Günter Hein, head of Europe’s Galileo Operations and Evolution.
By Inside GNSSIn this article, we will take a look at the various GNSS signals from the perspective of their cost-benefit tradeoffs. First, we’ll look at the evolution of consumer GPS architecture to date — where acquisition speed and sensitivity have been the main drivers of receiver architecture. That architecture has evolved rapidly to take full advantage of the characteristics of the GPS C/A code.
By Inside GNSS ESA Galileo IOV Test campaign authors, from left: Jörg Hahn, Stefano Binda, Edward Breeuwer, Roberto Prieto-Cerdeira, Marco Falcone, Alexander Mudrak, Gustavo Lopez- Risueño, Francisco Javier Gonzalez Martinez, and Daniel Blonski.
ESA Galileo IOV Test campaign authors, from left: Jörg Hahn, Stefano Binda, Edward Breeuwer, Roberto Prieto-Cerdeira, Marco Falcone, Alexander Mudrak, Gustavo Lopez- Risueño, Francisco Javier Gonzalez Martinez, and Daniel Blonski.The objective of the IOV phase was to launch the first four operational Galileo satellites and to deploy the first version of a completely new ground segment. During this phase, the European Space Agency (ESA) needed to validate — in the operational environment — all space, ground, and user components and their interfaces, prior to full system deployment. With the assistance of industry partners, ESA had to analyze the performance of the Galileo system and its components with the objective to refine the full operational capability (FOC) system.
By Inside GNSS
Unmanned aerial vehicles or UAVs comprise a category of aircraft that fly without a human operator onboard. They are more popularly referred to by the misleading moniker “drones,” which masks the wide variety in their design and capability.
By Inside GNSS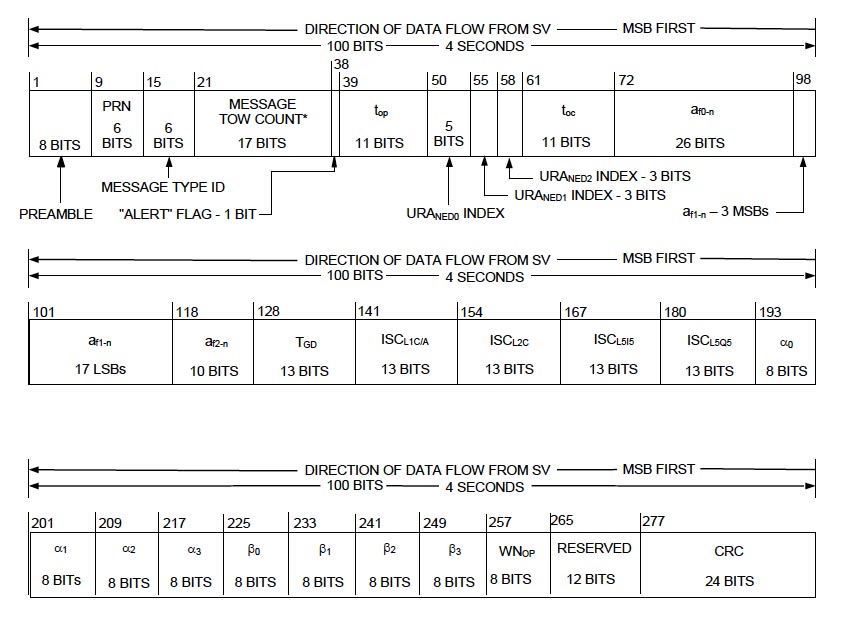 Message Type 30: satellite clock data, and corrections for ionospheric and group delay. From IS–GPS–200G
Message Type 30: satellite clock data, and corrections for ionospheric and group delay. From IS–GPS–200GIn a Federal Register notice issued today (March 5, 2014), the U.S. Department of Transportation (DoT) invited public comments on U.S. Air Force plans to implement preoperational L2C and L5 civil navigation (CNAV) messages on GPS Block IIR-M and IIF satellites next month.
By Inside GNSS