The fourth satellite of Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System, IRNSS-1D, was launched toward its intended geosynchronous orbit (GSO) today (Saturday, March 28, 2015) onboard the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C27).
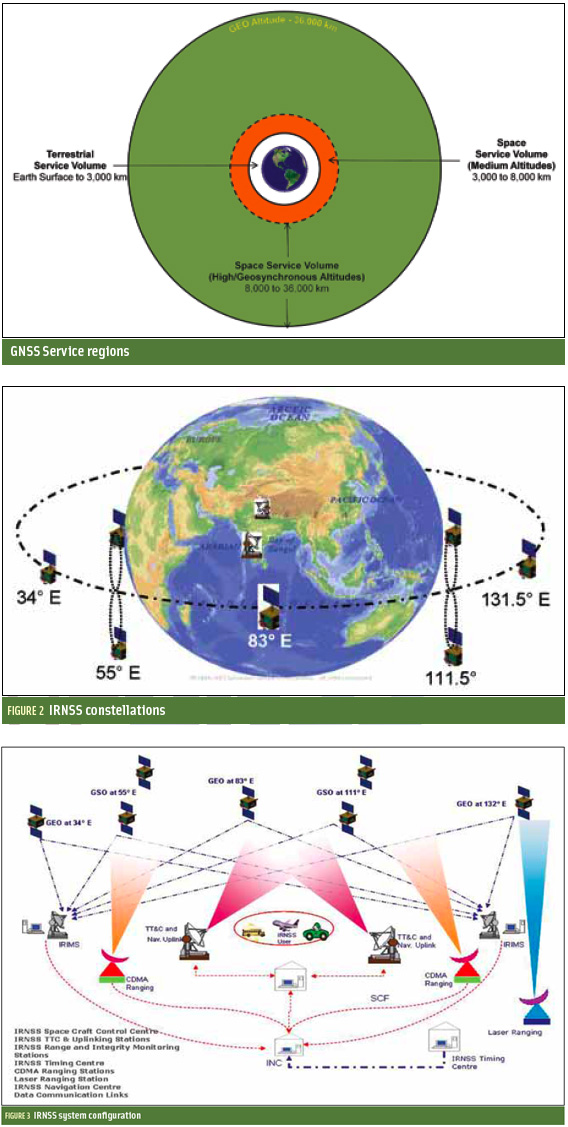
Seven satellites will comprise the IRNSS constellation being developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) to provide navigational services. IRNSS will help augment the satellite-based navigation system of India, which is currently under development and will provide navigation, tracking, and mapping services to the South Asia region.
The fourth satellite of Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System, IRNSS-1D, was launched toward its intended geosynchronous orbit (GSO) today (Saturday, March 28, 2015) onboard the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C27).
Seven satellites will comprise the IRNSS constellation being developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) to provide navigational services. IRNSS will help augment the satellite-based navigation system of India, which is currently under development and will provide navigation, tracking, and mapping services to the South Asia region.
The 1,425-kilogram spacecraft launched with the PSLV-C27 from the Satish Dhawan Space Center SHAR, Sriharikota, located about 80 miles from Chennai, India.
After a flight of about 19 minutes 25 seconds, the IRNSS-1D Satellite was injected to an elliptical orbit of 282.52 kilometers by 20,644 kilometers (very close to the intended orbit, according to ISRO) and successfully separated from the PSLV fourth stage.
After injection, the solar panels of IRNSS-1D were deployed automatically.
ISRO’s Master Control Facility (at Hassan, Karnataka) took over the control of the satellite. In the coming days, four orbit maneuvers will be conducted from Master Control Facility to position the satellite in the geosynchronous orbit at 111.75 degrees East longitude with 30.5 deg inclination.
IRNSS-1A, 1B and 1C, the first three satellites of the constellation, were successfully launched by PSLV on July 02, 2013, April 04, 2014, and October 16, 2014, respectively. All the three satellites are functioning satisfactorily from their designated orbital positions.
IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system designed to provide position information in the Indian region and 1,500 kilometers around the Indian mainland. IRNSS will provide two types of services based on signals transmitted in the L5 RF band: Standard Positioning Services (SPS) — provided to all users — and Restricted Services (RS), provided to authorized users.
In the coming months, the next satellite of this constellation, IRNSS-1E, is scheduled to be launched by PSLV. ISRO expects to have the entire IRNSS constellation of seven satellites completed by 2016.