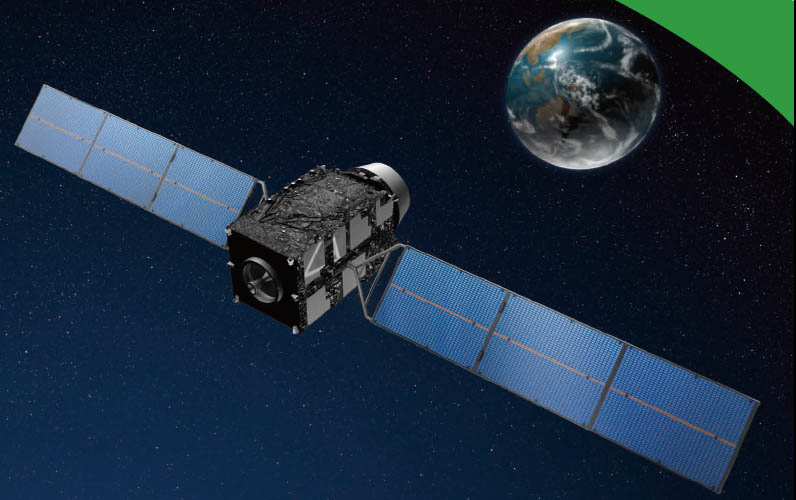
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation and NEC Corporation have received contracts to build the spacecraft and ground control system, respectively, for Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS).
The Japanese Cabinet Office announced the contract awards last Friday (March 29, 2013).
Mitsubishi will receive ¥50 billion (US$540 million) for building one geostationary satellite and two additional quasi-zenith satellites (QZSs) to join “Michibiki,” the first QZS launched on September 11, 2010.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation and NEC Corporation have received contracts to build the spacecraft and ground control system, respectively, for Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS).
The Japanese Cabinet Office announced the contract awards last Friday (March 29, 2013).
Mitsubishi will receive ¥50 billion (US$540 million) for building one geostationary satellite and two additional quasi-zenith satellites (QZSs) to join “Michibiki,” the first QZS launched on September 11, 2010.
The special purpose company— led by NEC and supported by Mitsubishi UFJ Lease & Finance and Mitsubishi Electric Corporation — established to build out the ground control segment under a private finance initiative will receive about ¥117 billion (US$1.3 billion). This will fund design and construction of the ground system and operation of the system for 15 years.
Each satellite will transmit the following signals: L1 C/A, L1C, L2C, L5, L1S (formerly called L1-SAIF for L1-Submeter-class Augmentation with Integrity Function) as well as L6a (a public regulated service), L5S (an augmentation signal on the GPS L5 frequency), and L6b (formerly called LEX, L-band Experimental, a high-accuracy augmentation signal centered at 1278.75MHz, the same as Galileo E6). Plans call for the system to finish its in-orbit test by March 2018.
The official announcement can be found on the Cabinet Office website (Japanese language only).