The European Commission (EC) — with the support of the European Space Agency (ESA) — has launched the procurement process for Galileo with an invitation to companies to submit requests for participation as prime contractors for six work packages (WPs) valued at €2.145 billion (US$3.39 billion).
The deadline for replying to the invitation is August 7.
The European Commission (EC) — with the support of the European Space Agency (ESA) — has launched the procurement process for Galileo with an invitation to companies to submit requests for participation as prime contractors for six work packages (WPs) valued at €2.145 billion (US$3.39 billion).
The deadline for replying to the invitation is August 7.
In a resolution on space and security passed by a large margin on July 10, the European Parliament endorsed the use of Galileo, particularly the public regulated service or PRS, as necessary for autonomous operations under the European Security and Defense Policy — perhaps the most forthright statement of support for prospective use of the civil-controlled GNSS system for military purposes.
In the meantime, Galileo program scientists and independent researchers continue to track and test the signals being transmitted by the latest Galileo experimental satellite, GIOVE-B. Articles in the forthcoming September/October issue of Inside GNSS will discuss the latest results of in-orbit tests of GIOVE-A and –B, drawing in part on data collected using a 25-meter dish antenna at Chilbolton in the United Kingdom.
Two Delft University of Technology faculty members, Christian Tiberius and Hans van der Marel, working with engineers at Belgian GNSS receiver manufacturer Septentrio, have reported successful calculation of Galileo-only double-difference carrier phase integer ambiguity measurements using L1 Open Service signals from the two GIOVE spacecraft. That work will also be described in an article in the September/October issue [of Inside GNSS magazine].
ESA will act as the Galileo procurement and design agent for the EC, which is the program manager and contracting authority of the publicly financed project. The process will follow a distinctively European process that includes a “competitive dialog” between ESA and the prospective prime contractors.
Under the current schedule, within seven weeks following the RTP deadline ESA will approve a short list of companies that will be invited to submit preliminary proposals on the work packages and take part in a dialog. After vetting during an intermediate dialog phase, selected companies will offer “refined proposals.”
The new procurement plan seems to relegate non-European companies to subcontract status. But some U.S. companies would like to be able to compete for the lead contracts for the Galileo satellites, for instance.
However, the tender guidelines limit prime contracts in the Galileo FOC procurement to “natural or legal persons established in one of the Member States of the European Union.” Moreover, subcontractors providing goods or services related to EU or national security must also be from the EU. In “exceptional circumstances,” ESA may authorize the use of non-EU subcontractors.
The competitive dialog phase is projected to take 15–30 weeks at the end of which successful companies will be invited to submit best and final offers (BAFOs) and supporting documentation. Contract awards would follow within three weeks, according to the current plan; however, the EC and ESA emphasize that the proposed timeline is “purely indicative” and may be shortened or lengthened.
Individually, the following estimated values have been earmarked for the six work packages:
• WP 1: System Support: €120 million
• WP2: Ground Mission Segment: €270 million
• WP 3: Ground Control Segment: €45 million
• WP 4: Space Segment (satellites): €840 million
• WP 5: Launch Services: €700 million
• WP 6: Operations €170 million
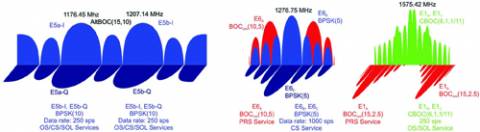
The overall program objective for Galileo is the deployment, by 2013, of a full operational capability (FOC) GNSS system comprising 30 satellites and ground facilities. The FOC Galileo system will provide five main services: Open Service, the Safety of Life Service, the Commercial Service, the Public Regulated Service (PRS), and the Search and Rescue Service.
Wanted: GNSS Advisor. Earlier, the EC Directorate-General for Energy and Transport (DG-TREN) issued an invitation to tender (ITT) for an advisor on the European GNSS program.
With a one-year term renewable up to three times, the contract will be designed to provide a pool of experts and organizations for review and counsel on administrative, financial, strategic and technical matters.