October 6, 2007
 Boeing technicians and first Block IIF satellite
Boeing technicians and first Block IIF satellite
The Boeing Company has successfully assembled and integrated all flight hardware onto the first GPS Block IIF (follow-on generation) satellite. Launch is now scheduled for the second half of 2008.
GPS llF spacecraft will bring new capabilities to the GPS constellation, such as a new encrypted military code, a new civil signal, crosslink enhancements, increased signal power, and longer design life. Boeing is building 12 GPS Block IIF satellites under contract from the GPS Wing at the Space and Missile Systems Center at Los Angeles Air Force Base.
Read More >
By Glen Gibbons
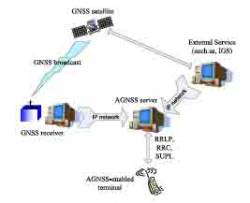 AGNSS Technique. Nokia graphic
AGNSS Technique. Nokia graphic